Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ANIMAL KINGDOM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - B (DIFFERENCE/SCIENTIFIC REASONS)|16 VideosANIMAL KINGDOM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - C (DEFINITION/EXPLANATION - TERMS/LOCATION - FUNCTION)|32 VideosANATOMY OF FLOWERING PLANTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTIONS FROM MODULE (QUESTION PAPER)|10 VideosBIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise OBJECTIVE SECTION (FILL IN THE BLANKS)|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-ANIMAL KINGDOM-OBJECTIVE SECTION (FILL IN THE BLANKS)
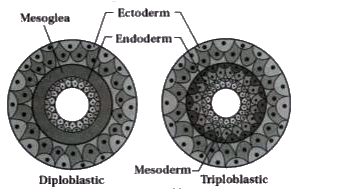
- Describe Diploblastic and Triploblastic organisation in animals.
Text Solution
|
- Teeth are modified ........... which are ........... directed
Text Solution
|
- Air bladder is present which regulates ....... in osteichthyes.
Text Solution
|
- Skin is ............ without gland except the ............. at the bas...
Text Solution
|
- Long Bones in birds are hollow with (pneumatic)
Text Solution
|
- The digestive tract of birds has additional chambers ........... &.......
Text Solution
|
- Snakes and lizards shed their scales as ......
Text Solution
|
- ....... represents ear in Reptilia.
Text Solution
|
- Name aquatic annelida.
Text Solution
|
- Alimentary canal is complete with well developed ............ in Asche...
Text Solution
|
- Pharynx is perforated by ............ in chordates.
Text Solution
|