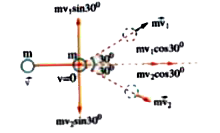
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COLLISIONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|12 VideosCOLLISIONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise NUMERICAL EXERCISE ( LEVEL 1)|18 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED))|3 VideosELASTICITY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Questions for Descriptive Answers|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-COLLISIONS -QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
- A ball moving with a velocity of 6 m/s strikes an identical stationary...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical balls A,B,C and D are placed in a line on a frictionles...
Text Solution
|
- Two beads A and B of masses m, and m, respectively are threaded on a s...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 100g is projected vertically upwards from the ground wi...
Text Solution
|
- A shell flying with velocity v = 500 ms^(-1) bursts into three identi...
Text Solution
|