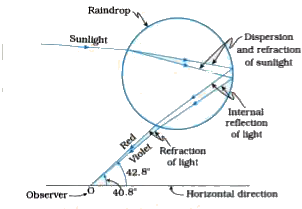
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise TEXTUAL EXERCISE|13 VideosTHE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS|9 VideosQUESTION PAPER-2 (MARCH,2020 - BOARD'S QUESTIONS PAPER)
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - D (Answer the following questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD-Practical Skill Based Questions with Answers
- A rainbow is an example of dispersion of sunlight. Justify this statem...
Text Solution
|
- Dispersion is caused by refraction and not by reflection. Why?
Text Solution
|
- A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split up into seve...
Text Solution
|
- When a beam of white light is passed through a triangular glass prism,...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow beam PQ of white light passes through a glass prism ABC as sh...
Text Solution
|
- (a) A narrow beam of white light is incident on three glass objects as...
Text Solution
|