A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (Answer the following questions in very short as directed (Miscellaneous) )|55 VideosTHE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Value Based Questions With Answers|24 VideosTHE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS|3 VideosQUESTION PAPER-2 (MARCH,2020 - BOARD'S QUESTIONS PAPER)
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section - D (Answer the following questions)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-THE HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD-OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (Choose the correct option)
- Which phenomenon can explain the advance sunrise and the delayed sunse...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following phenomena cannot be explained by scattering of ...
Text Solution
|
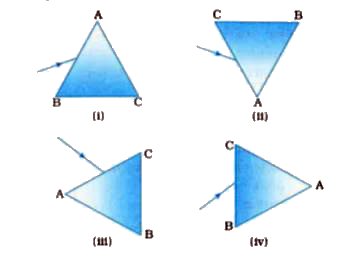
- The base of an equilateral triangle ABC is BC. When it is arranged in ...
Text Solution
|
- The Sun appears white in afternoon. The reason is ..........
Text Solution
|
- Sea water at more depth appears blue. The reason is …….....
Text Solution
|
- When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes ......... a...
Text Solution
|
- When the ciliary muscles contract, the eye lens becomes ......... and ...
Text Solution
|
- The rainbow on the moon …
Text Solution
|
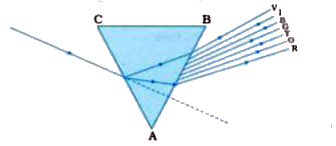
- In dispersion of white light due to a triangular glass prism, the devi...
Text Solution
|
- Which lens from the following, should a person suffering from near-sig...
Text Solution
|
- Which lens is used by a person suffering from far-sightedness?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true for near sightedness?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is true for far- sightedness?
Text Solution
|
- Where is the image formed in the eye of a person suffering from far si...
Text Solution
|
- A person has a defect of eye vision. His near point is 40 cm. It means...
Text Solution
|
- A person has a defect of vision. His far point is 1.5 m. It means...
Text Solution
|
- Out of the following, which light is deviated minimum in the dispersio...
Text Solution
|
- Which light has maximum speed in glass?
Text Solution
|
- Which ray of light is present exactly at the middle of the spectrum ob...
Text Solution
|
- The lens in human eye is a ...........
Text Solution
|