Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-TRIANGLES-OTHER IMPORTANT EXAMPLES
- In the given figure, CD||LA" and "DE||AC. Find the length of CL if BE=...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, PQ||BA" and "PR||CA. If PD= 12 cm, find BD xx CD.
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, AB||DE" and "BD||EF. Prove that DC^(2)= CF xx AC.
Text Solution
|
- ABC is a triangle with AB= AC and D is a point on AC such that BC^(2)=...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, find the value of x in terms of a, b and c.
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, DeltaABR ~ DeltaPQR. If PQ= 30 cm, AB= 45 cm, AP=...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, DE||BC. If DE : BC = 3 : 5, find (ar(ADE))/(ar(BC...
Text Solution
|
- The areas of two similar triangles are 121 cm^(2) and 64 cm^(2) respec...
Text Solution
|
- In DeltaABC, /B= 90^(@), BM bot AC, BC= 5 cm and AC = 12 cm. Find the ...
Text Solution
|
- In a quadrilateral ABCD, /B= 90^(@)" and "AD^(2)= AB^(2)+BC^(2)+CD^(2)...
Text Solution
|
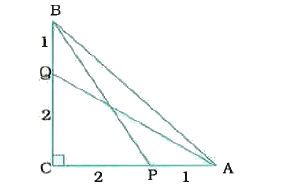
- In a right trianlge ABC right angled at C, P and Q are the points on t...
Text Solution
|
- In triangleABC, AD, BE, CF are the medians. Prove that, 4(AD^(2)+BE^(2...
Text Solution
|