A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISM-All Questions
- Grafting is the union between two plants of closely related varieties....
Text Solution
|
- Given figures illustrate.
Text Solution
|
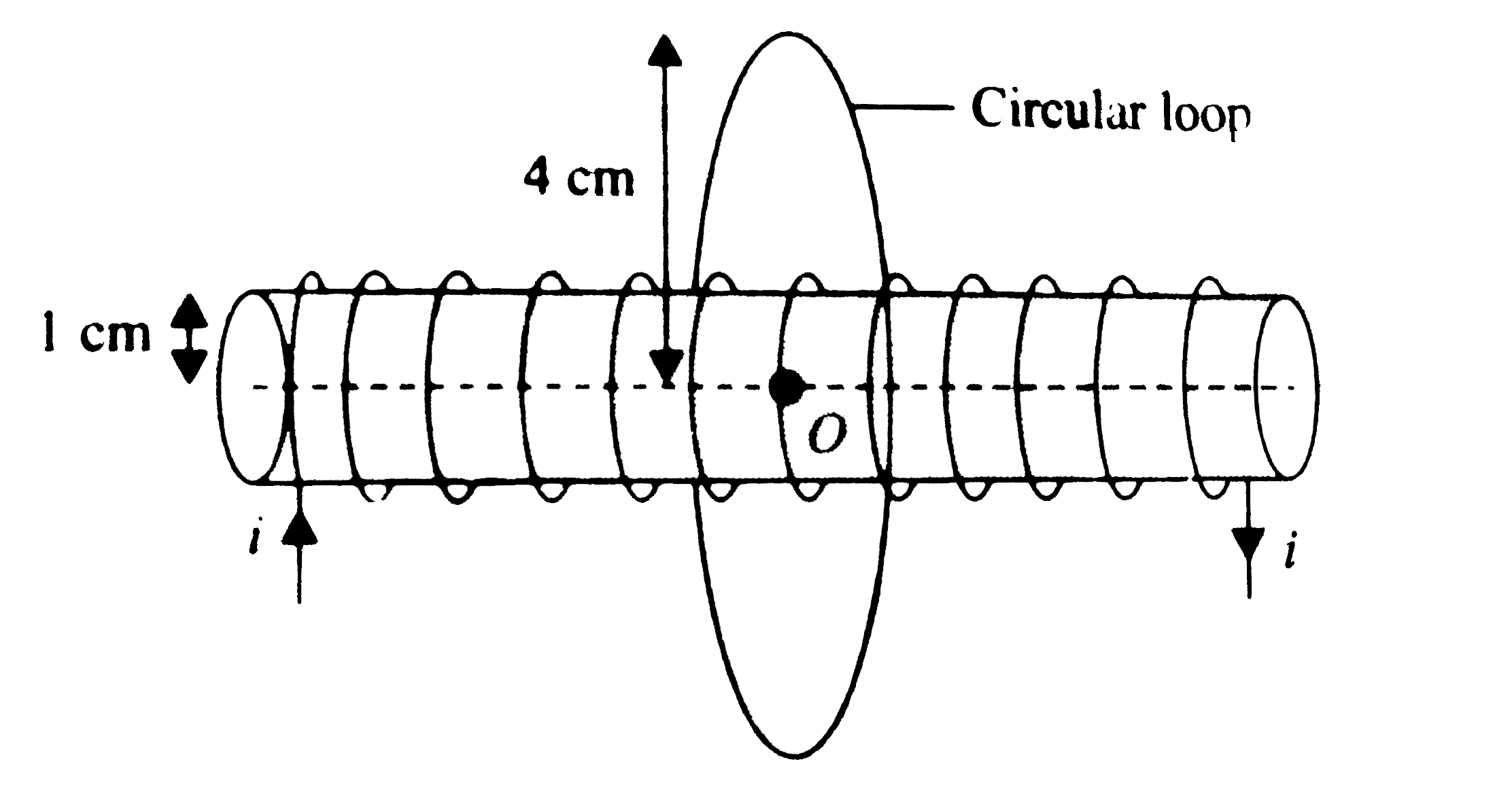
- A long solenoid having n = 200 turns per metre has a circular cross-se...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is wheat fruit?
Text Solution
|
- In these figures, two life-cycles are described. Mark the correct opti...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure given below, two particles of masses m and 2m are fixed ...
Text Solution
|
- The term "Linkage" was coined by
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m=3kg, are connected with t...
Text Solution
|
- A few statements with regard to sexual reprodction are given below. ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of formation of new organic matter by rabbit in a grass land ...
Text Solution
|
- The pressures at A and B in the atmosphere are, respectively,
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct statements.
Text Solution
|
- Fill in blanks (w.r.t. experimental material used by Morgan) (i) Fem...
Text Solution
|
- If three uniform spheres, each having mass M and radius R, are kept in...
Text Solution
|
- The value of escape speed from the surface of earth is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements, support the view that elaborate sex...
Text Solution
|
- Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variation than th...
Text Solution
|
- Pick out the correct statement from the following
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is suspended from one end of a light spring as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Phenotype of an organism is the result of
Text Solution
|