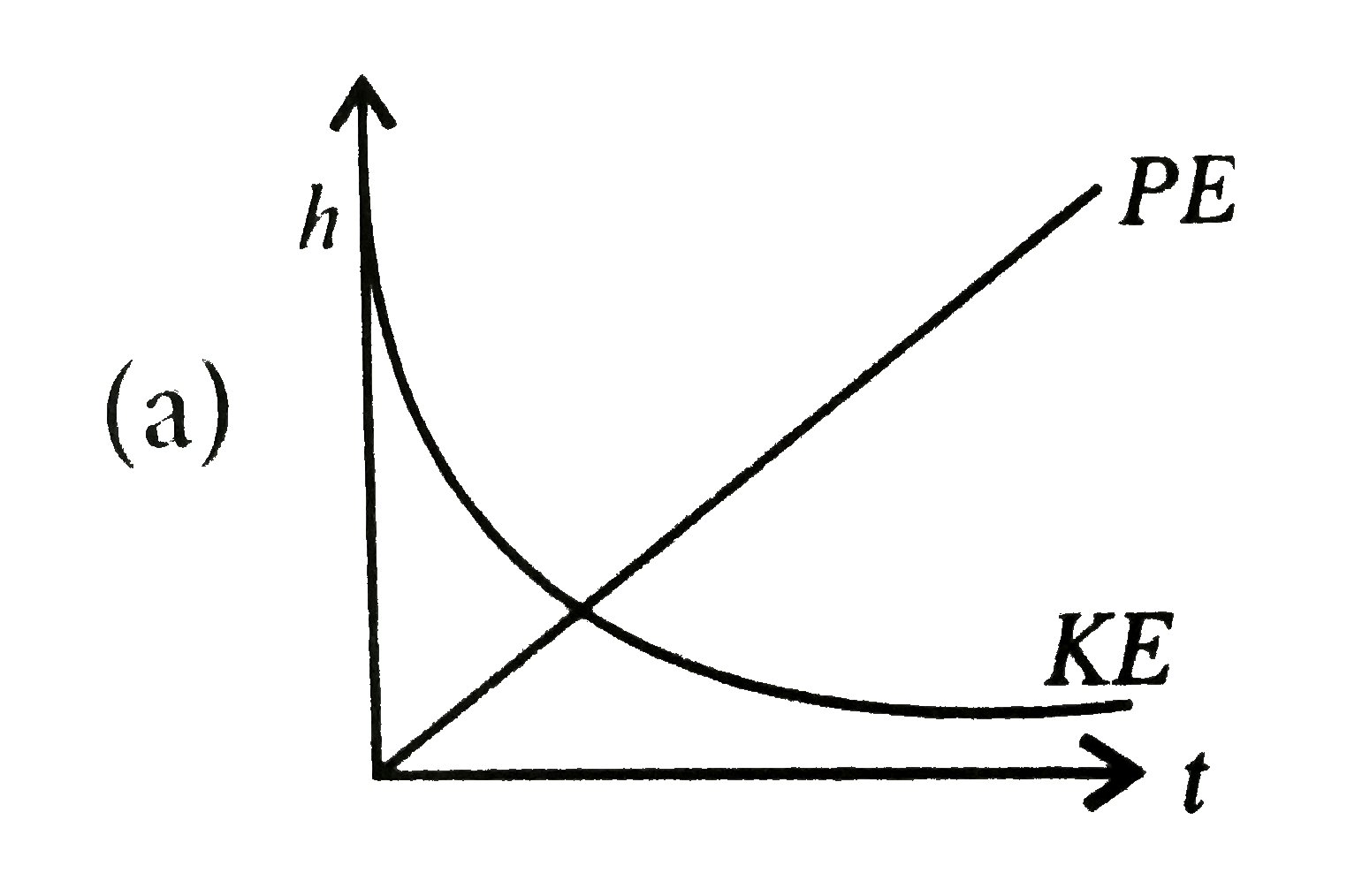
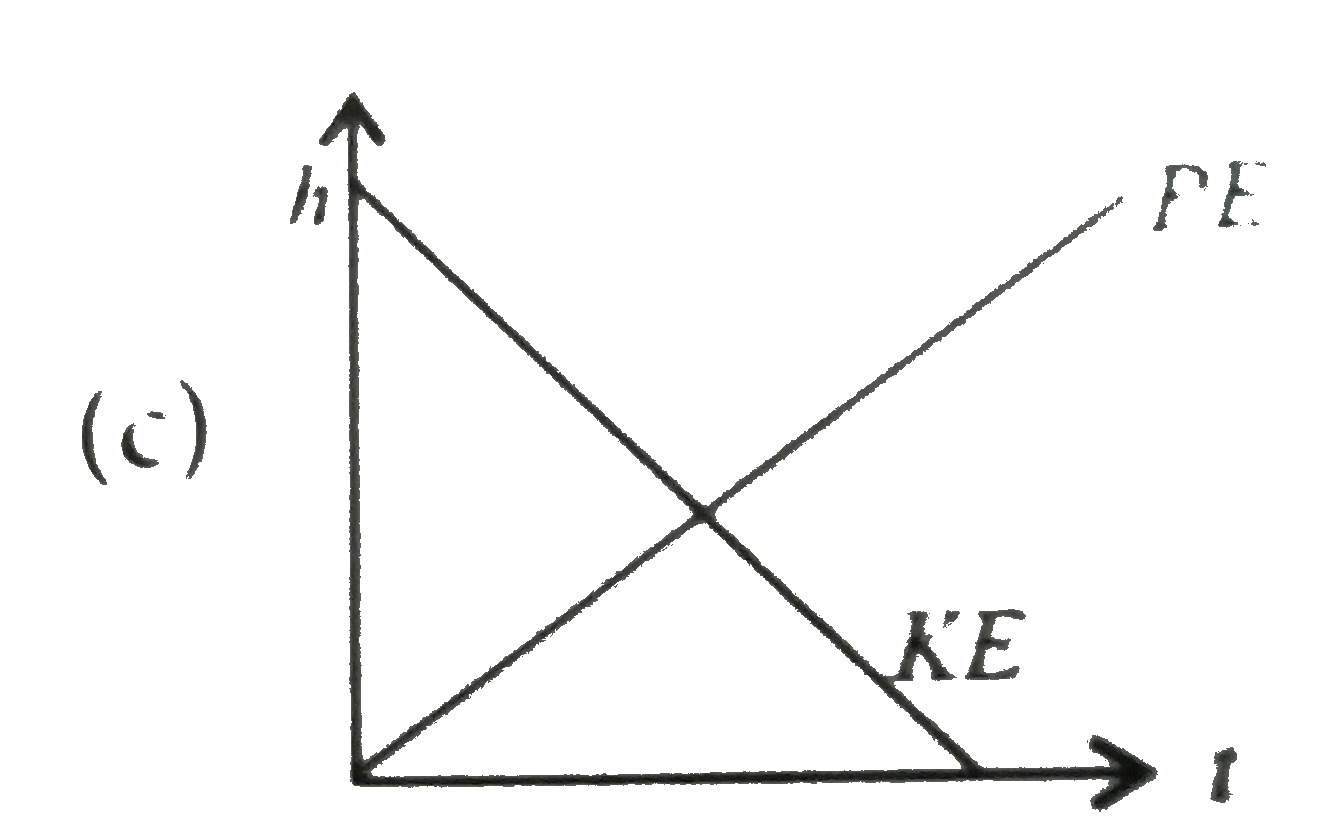
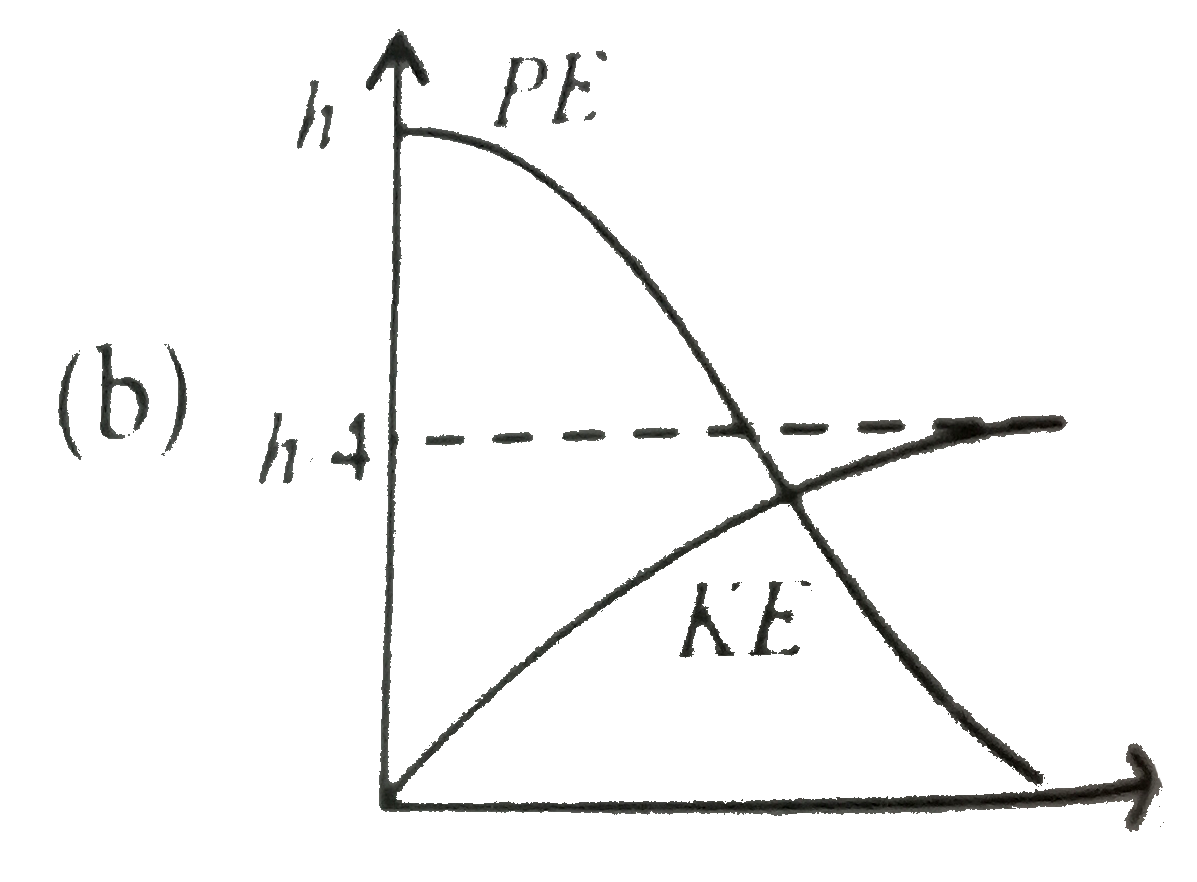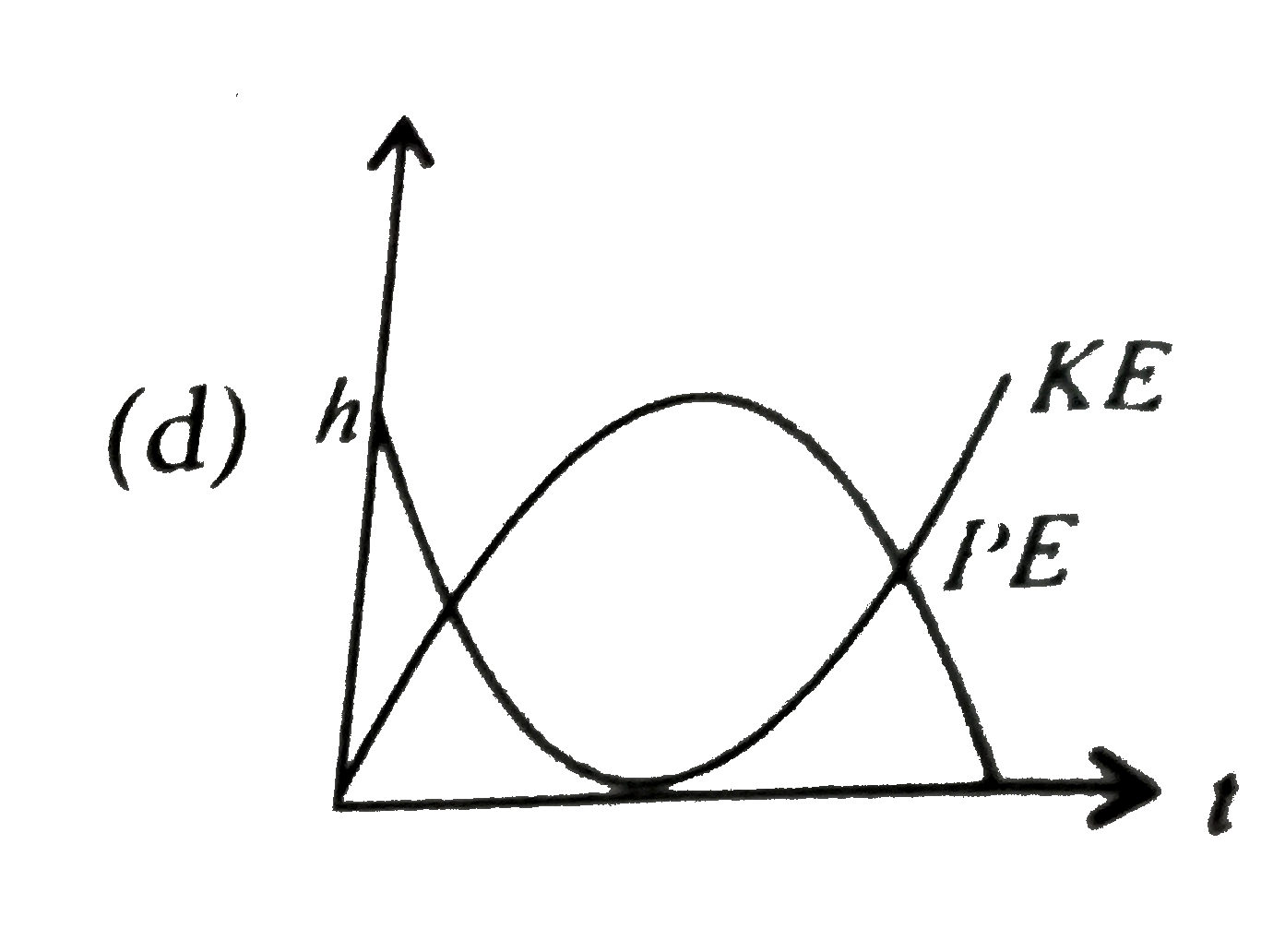A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK , ENERGY AND POWER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|15 VideosWORK , ENERGY AND POWER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Motion Of Work And Kinetic Energy : The Work-Energy Theorem|4 VideosWORK , ENERGY AND POWER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosWAVES
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-WORK , ENERGY AND POWER-NCERT
- An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forc...
Text Solution
|
- A proton is kept at rest. A positively charged particle is released fr...
Text Solution
|
- A man squatting on the ground gets straight up and stand. The force of...
Text Solution
|
- A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the...
Text Solution
|
- A body is falling freely under the action of gravity alone in vacuum. ...
Text Solution
|
- During inelastic collision between two bodies, which of the following ...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet...
Text Solution
|
- The potential energy function for a particle executing linear SHM is g...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity v= kx^(...
Text Solution
|
- A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of c...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the diagrams shown in figure. Most closely shows the variatio...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the diagram shown in figures respresents variation of total m...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of 5kg is moving along a circular path or radius 1m. If the mas...
Text Solution
|
- A raindrop falling from a height h above ground, attains a near termin...
Text Solution
|
- In a shotput event an athlete throws the shotput of mass 20 kg with an...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the diagrams in figure, correctly shows the change in kineti...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150g moving with a speed of 126km//h hits at th...
Text Solution
|