A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise The Gravitational constant|8 VideosGRAVITATION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Acceleration due to gravity below and above the surface of earth|8 VideosGRAVITATION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosKINETIC THEORY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-GRAVITATION-Universal law of Gravitations
- Which of the following statements is correct regarding the gravitation...
Text Solution
|
- Match the Column I with Column II
Text Solution
|
- A mass m is placed at point P lies on the axis of a ring of mass M and...
Text Solution
|
- Two sphere of masses m and M are situated in air and the gravitational...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass m is placed inside a spherical shell of radius R and mass...
Text Solution
|
- Two stars of mass m(1) and m(2) are parts of a binary star system. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical spheres each of mass M and Radius R are separated by a d...
Text Solution
|
- Three masses each of mass m are palced at the vertices of an equilater...
Text Solution
|
- In the question number 25, if the mass placed at vertex A is doubled, ...
Text Solution
|
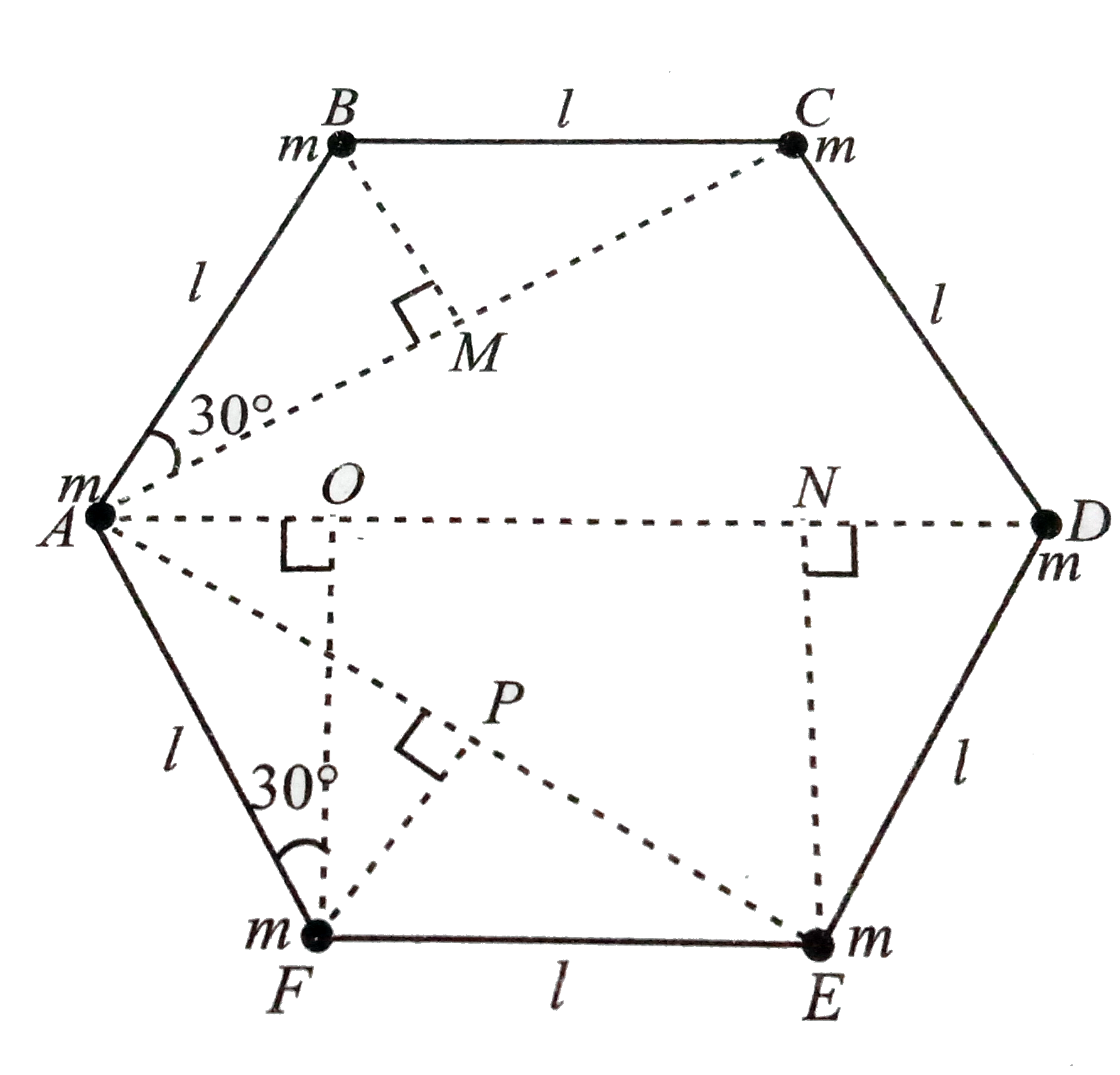
- Six point masses of mass m each are at the vertices of a regular hexag...
Text Solution
|
- Two point masses A and B having masses in the ratio 4:3 are separated ...
Text Solution
|
- A research satellite of mass 200 kg circles the earth in an orbit of a...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of moon 1% of mass of earth. The ratio of gravitational pull ...
Text Solution
|
- Imagine a light planet revolving around a very massive star in a circu...
Text Solution
|