A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
KINETIC THEORY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Kinetic Theory of An Ideal Gas|18 VideosKINETIC THEORY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise LAW OF EQUIPARTITION OF ENERGY|5 VideosKINETIC THEORY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|10 VideosGRAVITATION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-KINETIC THEORY-BEHAVIOUR OF GASES
- A real gas behaves like an ideal gas if its
Text Solution
|
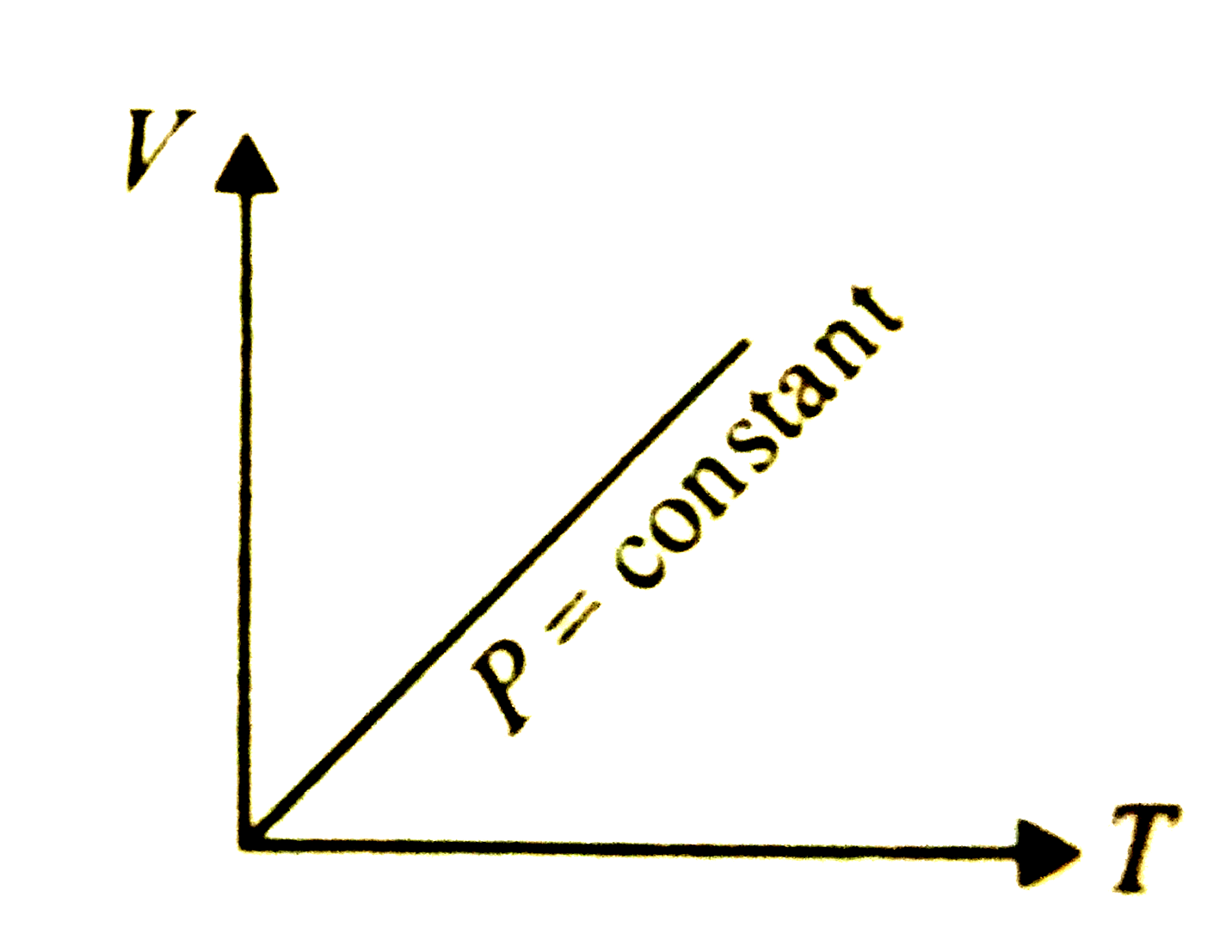
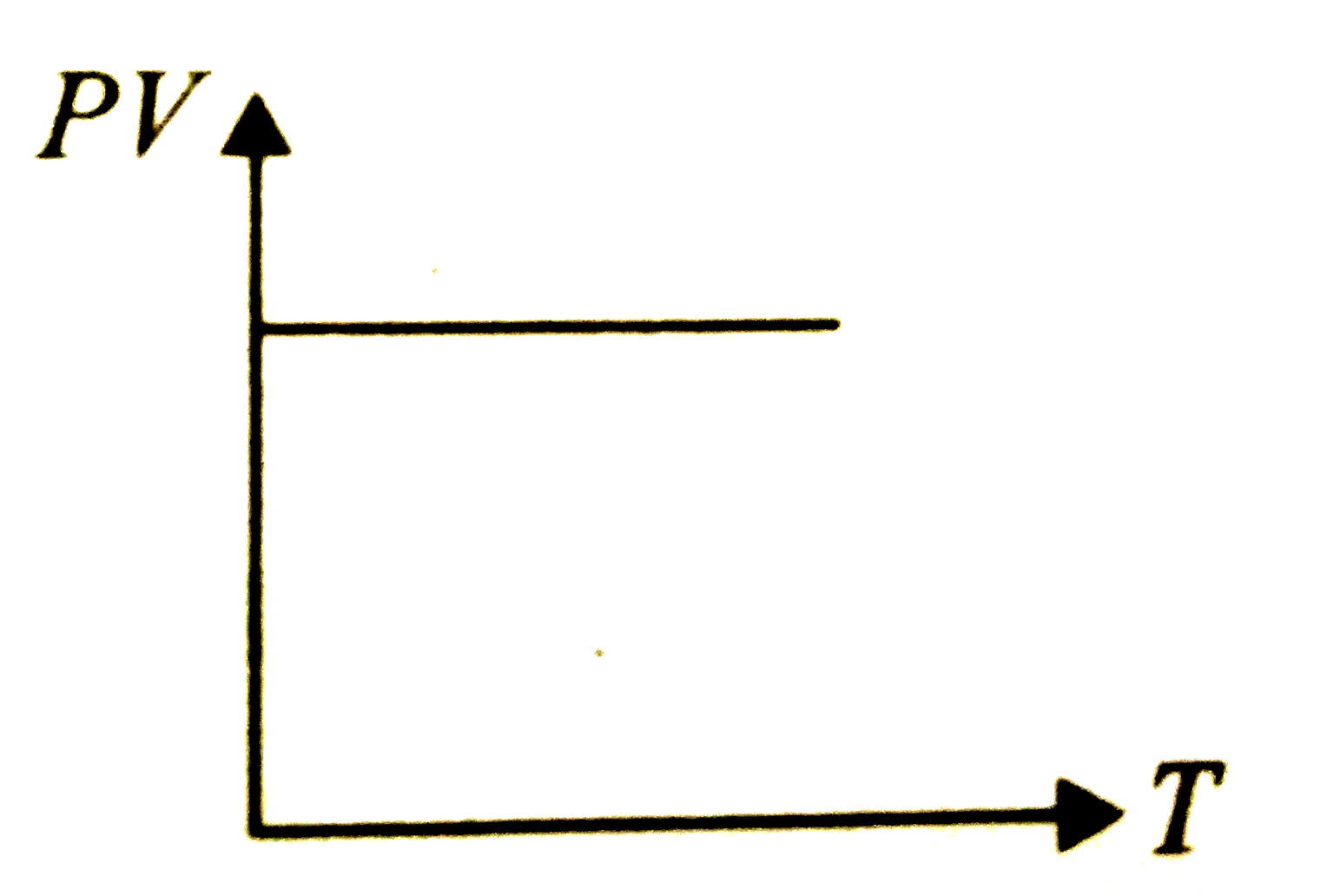
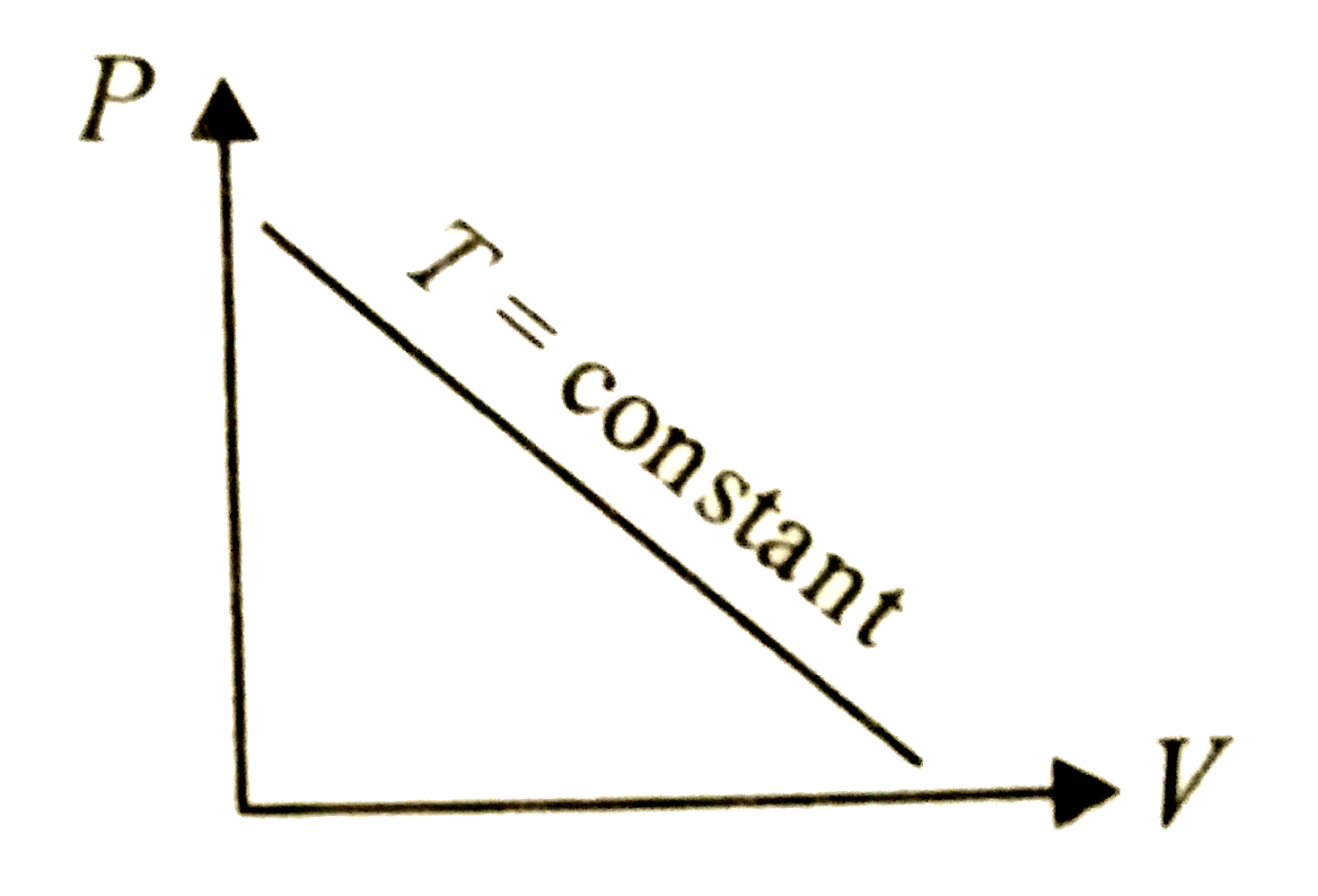
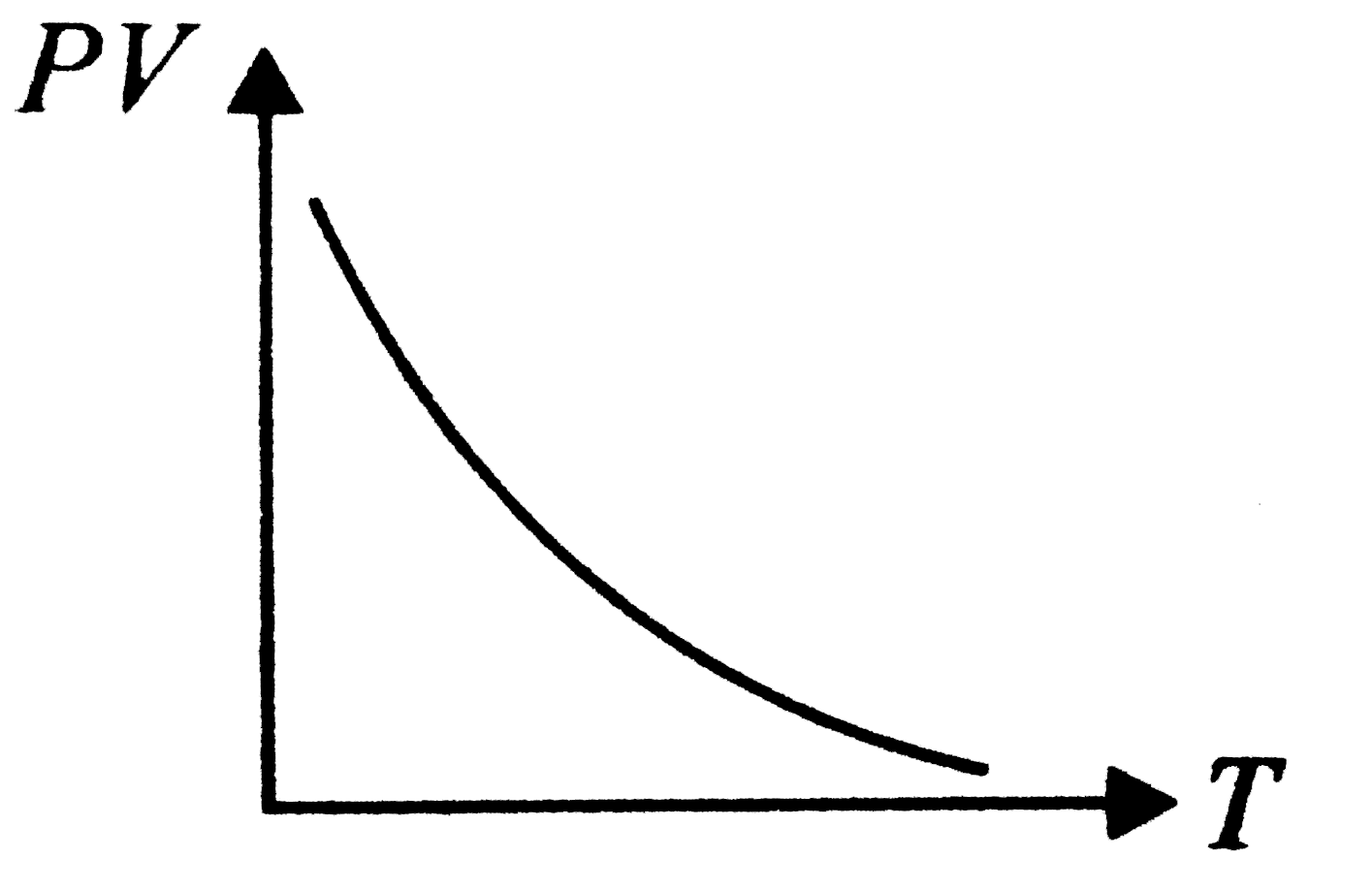
- Which of the following graphs represent the behaviour of an ideal gas ...
Text Solution
|
- If the pressure and the volume of certain quantity of ideal gas are ha...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble of volume 1.0 cm^(3) rises from the bottom of a lake 40 ...
Text Solution
|
- The diameter of an oxygen molecule is 3 Ã… The ratio of molecular volu...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon contains 1500 m^(3) of helium at 27^(@)C and 4 atmospheric p...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas of equal number of m...
Text Solution
|
- Given is the graph between (PV)/T and P for 1 gm of oxygen gas at two ...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel has 6gm of oxygen at pressure P and temperature 400 K.A smal...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel has 6g of hydrogen at pressure P and temperature 500K. A smal...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains two non-reactive gases neon (monoatomic) and oxygen ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder contained 10kgof gas at pressure 10^(7) N / m^(2). The quan...
Text Solution
|
- A gas at 300 K has pressure 4 xx 10^(-10) N//m^(2). IF k = 1.38 xx 10^...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of vessel A is twice the volume of another vessel B and bot...
Text Solution
|
- When the temperature of a gas, filled in a closed vessel is increased ...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of state for 5 g of oxygen at a pressure P and temperatur...
Text Solution
|
- A vessel contains 1 mole of O2 gas (relative molar mass 32) at a tempe...
Text Solution
|
- In a certain region of space there are only 5 gaseous molecules per cm...
Text Solution
|
- A sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume V at pressure P and absolut...
Text Solution
|
- One half mole each of nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide are mixed in...
Text Solution
|