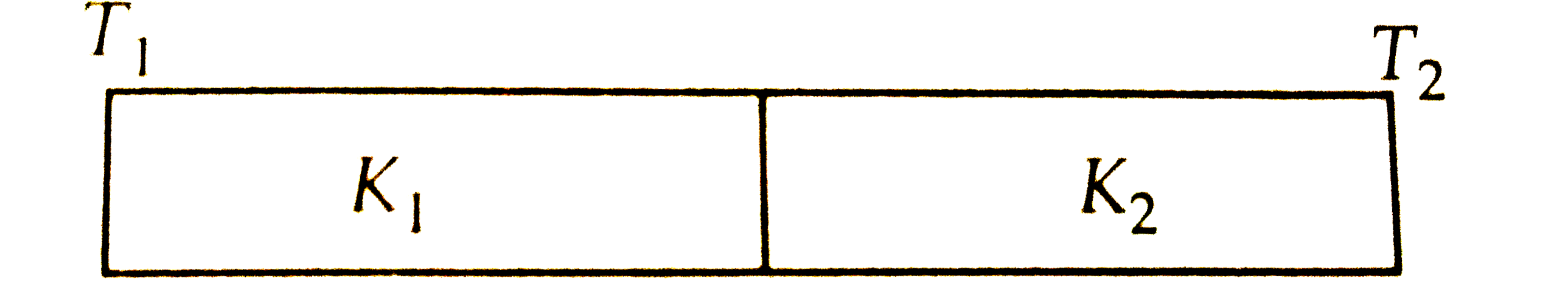
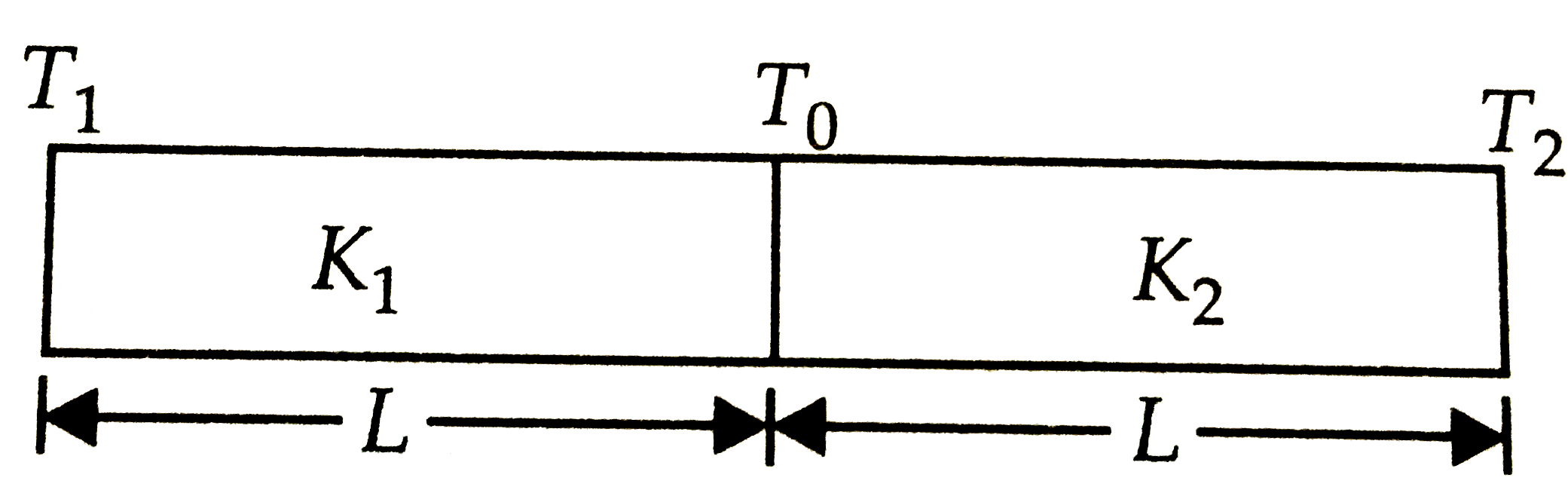
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Higher Order|8 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Exampler Problems|8 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Change of State|13 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|8 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Heat Transper
- One end of a 0.25 m long metal bar is in steam and the other is in con...
Text Solution
|
- A pan filled with hot food cools from 94^(@)C to 86^(@)C in 2 minutes ...
Text Solution
|
- Two bars of same length and same cross-sectional area but of different...
Text Solution
|
- In the question number of 45, the equivalent thermal conductivity of t...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a compound slab consisting of two different material having e...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods of equal length and diameter have thermal conductivite 3 and ...
Text Solution
|
- Three metal rods of the same material and identical in all respect are...
Text Solution
|
- Three very large plates of same area are kept parrallel and close to e...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical ice box of side 50 cm has a thickness of 5.0 cm. if 5 kg of ...
Text Solution
|
- A wall has two layers A and B, each made of different material. Both t...
Text Solution
|
- Mud houses are cooler in summer and warmer in winter because
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the v(m) = T graph for a perfectly black bod...
Text Solution
|
- The equatorial and polar regions of the earth receive unequal sol...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following process, convection does not take place pri...
Text Solution
|
- Wien's displacment law expresses relation between
Text Solution
|
- If lambda(m) denotes
Text Solution
|
- A black body has maximum wavelength lambda(m) at temperature 2000 K. I...
Text Solution
|
- The thermal radiation from a hot body travels with a velocity...
Text Solution
|
- Experimental investigations show that the intensity of solar radiat...
Text Solution
|
- The wavelength of maximum intensity of radiation emitted by a star is ...
Text Solution
|