A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Factors Influencing Rate Of Reaction|30 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Integrated Rate Equation|25 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise ASSERTION & REASON|15 VideosBIOMOLECULES
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Rate Of A Chemical Reaction
- The rate of chemical reaction
Text Solution
|
- The minus sign in rate = - (d[A])/(dt) indicates the in concentration...
Text Solution
|
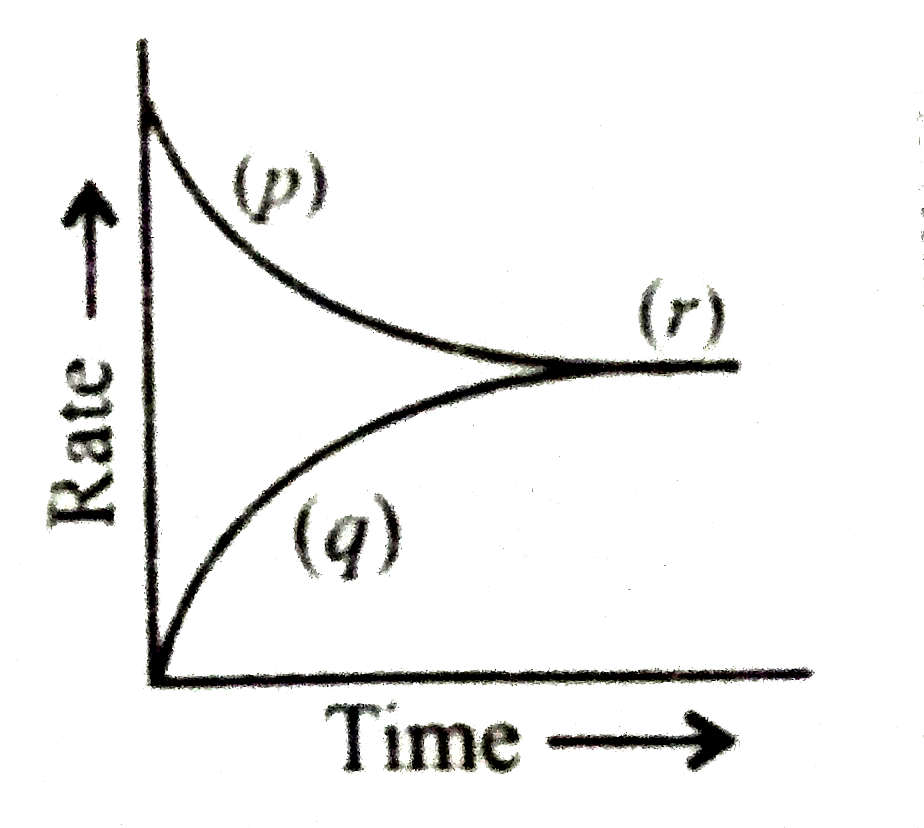
- For reversible reaction, A + B hArr C + D, the graph for rate of react...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction P + Q to 2R + S. Which of the following statements is i...
Text Solution
|
- For this reaction N(2(g))+3H(2(g))to2NH(3(g)) The relation be...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction, 2N(2)O(5)(g) to 4NO(2)(g) + O(2)(g) rate of reaction i...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 2N(2)O(4)iff 4NO(2), given that (-d[N(2)O(4)])/(dt)=...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NH(3)rarrN(2)+3H(2) , it is observed that (-d(NH(3)))/...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the reaction, 2N(2) O(5) to 4NO(2) + O(2) In the reaction NO(...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction R to P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0....
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction 2HI to H(2) + I(2) the concentration of HI decreases fro...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction 4NH(3) + 5O(2) to 4NO + 6H(2) O, if the rate of disap...
Text Solution
|
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO(2)) dissociates into nitric oxide (NO) and oxygen...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of disappearance of SO(2) in the reaction 2SO(2) + O(2) rarr ...
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction 2X to Y, the concentration of X decreases from 3.0 mole/...
Text Solution
|
- In a reaction, 2X to Y, the concentration of X decreases from 0.50M to...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction, 2N(2)O(5)to4NO(2)+O(2) rate and rate constant are 1....
Text Solution
|