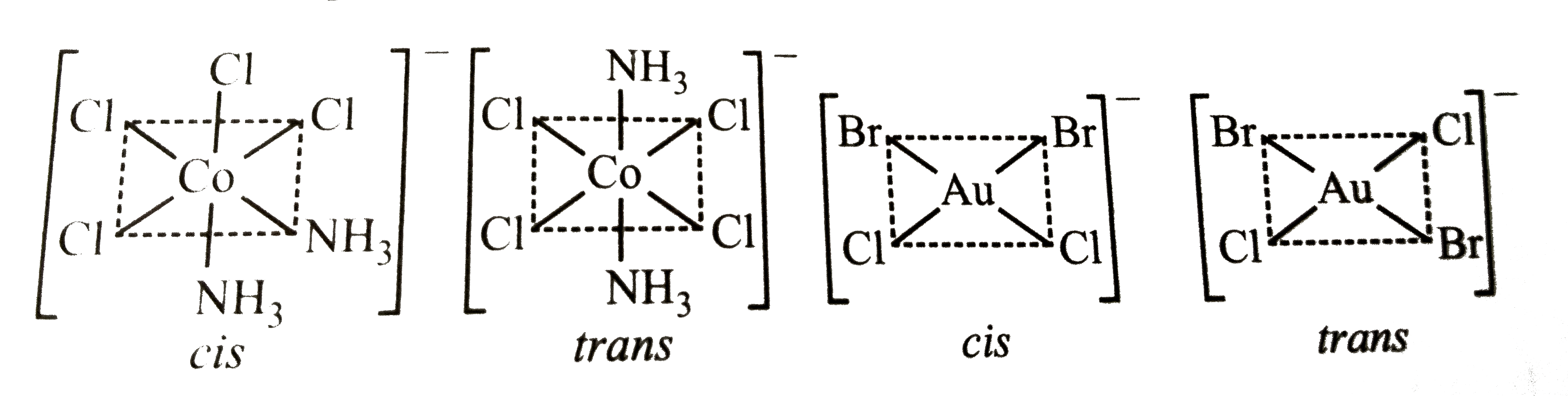A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise HOTS|8 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS|14 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|15 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS ENGLISH-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS -Assertion And Reason
- How many geometrical isomers are there for (a)[Co(NH(3))(2)CI(4)]^(Θ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Aqueous solution of the compound CoCl(3) * 4NH(3) when tre...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : The complex K(3) [Cr(C(2)O(4))(3)] when present in aqueous...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : N(CH(2)CH(2)NH(2))(3) and EDTA are examples of polydentate...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Coordination number of Fe and Co in [Fe(C(2) O(4))(3)]^(3-...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : [Co(NH(3))(5)Br]SO(4) gives white precipitate with barium ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Tetrahedral complexes having two different types of uniden...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In a coordination entity [PtCl(2)(en)(2)]^(2+) only the ci...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Inner orbital complexes are low spin complexes . Reason...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : [Fe(H(2)O)(6)]^(2+) is sp^(3) d^(2) hybridised and paramag...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In tetrahedral complexes low spin configuration are rarel...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : [Ti(H(2)O)(6)]Cl(3) on heating becomes colourless . Reas...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : According to crystal field theory , during complex formati...
Text Solution
|
- [Fe(H2O)6]^(3+) is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6]^(3-) is wea...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : K(2)[Ni(EDTA)] is more stable than K(3)[Al(C(2)O(4))(3)]. ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Geometrical isomerism is also called cis-trans isomerism ....
Text Solution
|