Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-I|11 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION A)(MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|5 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|35 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION-B) (VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)|4 VideosELECTROMAGNETICE INDUCTION
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise Self Assessment Test Section -D|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES-SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- When an ideal capacitor is charged by a d.c. battery, no current flows...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor, made of two parallel plates each of plate are A and separ...
Text Solution
|
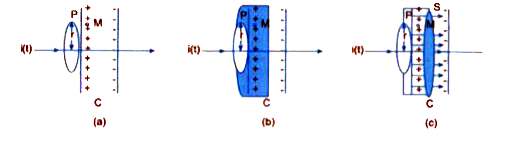
- Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of cha...
Text Solution
|
- An electromagnetic wave is travelling in a medium with a velocity vecv...
Text Solution
|
- How does a charge q oscillating at certain frequency produce electroma...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why are infra-red waves often called heat waves ? Explain. (b) W...
Text Solution
|
- The oscillating magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave is give...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary as (a) 10^...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths lie in the range ...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations in ascending order of...
Text Solution
|
- Write one method each of (i) production, and (ii) detection of microwa...
Text Solution
|
- Briefly state the working principle of microwave ovens.
Text Solution
|
- (a) Give one use of electromagnetic radiations obtained in nuclear dis...
Text Solution
|
- The following table gives the wavelength range of some constituents of...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why do welders wear special glass goggles or face masks with glass...
Text Solution
|
- How are infrared waves produced ? Why are these referred to as .heat w...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in the descending orde...
Text Solution
|
- Name the types of electromagnetic radiations which (i) are used in des...
Text Solution
|
- How does Ampere-Maxwell law explain the flow of current through a capa...
Text Solution
|
- Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show...
Text Solution
|