Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise TEXTUAL EXERCISE|21 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWER|6 VideosELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PRACTICAL SKILL BASED QUESTION WITH ANSWERS|20 VideosMODEL QUESTION PAPER 01
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT -VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
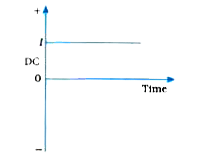
- Explain the direction current (DC).
Text Solution
|
- Shalini and his brother Amey observed a water-pump working , Shal...
Text Solution
|
- Shalini and his brother Amey observed a water-pump working , Shal...
Text Solution
|
- Shalini and his brother Amey observed a water-pump working , Shal...
Text Solution
|
- Jay.s friend Dev was playing and that too with a magnet . Jay asked ...
Text Solution
|
- Jay.s friend Dev was playing and that too with a magnet . Jay asked ...
Text Solution
|
- Jay.s friend Dev was playing and that too with a magnet . Jay asked ...
Text Solution
|
- Dharmendra is a welder , working at Amit.s house . After electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Dharmendra is a welder , working at Amit.s house . After electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Dharmendra is a welder , working at Amit.s house . After electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Bharat had an electric iron . He connected it into two - pin plug . Ob...
Text Solution
|
- Bharat had an electric iron . He connected it into two - pin plug . Ob...
Text Solution
|
- Bharat had an electric iron . He connected it into two - pin plug . Ob...
Text Solution
|
- Atul buit a small house . He used well - insulated copper wires of go...
Text Solution
|
- Atul buit a small house . He used well - insulated copper wires of go...
Text Solution
|
- Atul buit a small house . He used well - insulated copper wires of go...
Text Solution
|