Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWER|6 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ( ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN ONE WORD/SENTENCE:)|14 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS|15 VideosELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PRACTICAL SKILL BASED QUESTION WITH ANSWERS|20 VideosMODEL QUESTION PAPER 01
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT -TEXTUAL EXERCISE
- The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is…….
Text Solution
|
- The device used for producing electric current is called a……..
Text Solution
|
- The essential difference between and AC generator and a DC generato...
Text Solution
|
- At the time of short circuit , the current in the circuit……
Text Solution
|
- State whether the following statement are true or false : An elect...
Text Solution
|
- State whether the following statement are true or false : An elect...
Text Solution
|
- State whether the following statement are true or false : The mag...
Text Solution
|
- State whether the following statement are true or false : The wi...
Text Solution
|
- List two methods of producing magnetic fields .
Text Solution
|
- How does a solenoid behave like a magnet ? Can you determine the no...
Text Solution
|
- When is the force experienced by a current - carrying conductor pla...
Text Solution
|
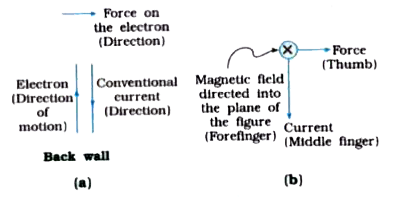
- Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with you back to one wall. ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor . Explain its princple ...
Text Solution
|
- Name some devices in which electric motors are used .
Text Solution
|
- A coil of insulated copper wire is conncted to a galvnometer . What...
Text Solution
|
- Two circular coil A and B are placed close to each other . If the c...
Text Solution
|
- State the rule to determine the direction of a (i) magnetic field pr...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric genera...
Text Solution
|
- When does an electric short circuit occur ?
Text Solution
|
- What is the function of an earth wire ? Why is it necessary to earth...
Text Solution
|