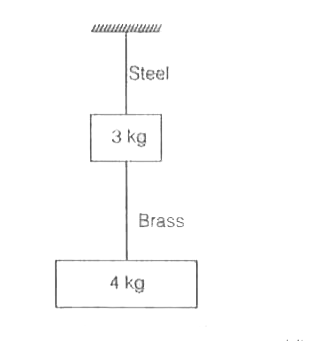
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The ratios of length areas of cross-section and Young's modulii of s...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of lengths, radii and Young's moduli of steel and brass w...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's modulus of steel is twice that of brass. Two wires of the ...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of lengths, radii and Young's moduli of steel and brass w...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of lengths, radii and young's modulii of steel and brass ...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's modulii of brass ans steel are in the ratio of 1 : 2. A br...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of lengths, radii and Young's modulus of steel and brass ...
Text Solution
|
- The Young's Modulus of steel is twice that of brass. Two wires of same...
Text Solution
|
- The ratios of length areas of cross-section and Young's modulii of ste...
Text Solution
|