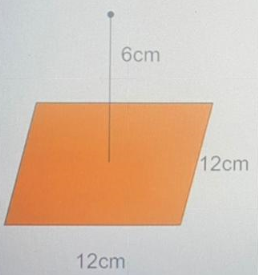
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find the flux of point charge q through the square surface ABCD as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Find the flux of point charge q through the square surface ABCD as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is placed at the corner of a square of side a. Find t...
Text Solution
|
- Eight point charges (can be assumed as small spheres uniformly charged...
Text Solution
|
- There is a point charge +q inside a hollow sphere and a point charge -...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q is placed at a distnace a/2 directly above the centre...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is placed at the centre of a hemisphere. Find the rat...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge Q is placed at the corner of a square of side a, then f...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge +q is placed at the centre of curvature of a hemisphere...
Text Solution
|