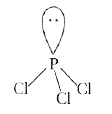Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -D (SOLUTIONS OF NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (MATCH THE COLUMNS )|5 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -D (SOLUTIONS OF NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (ASSERTION AND REASON)|3 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -D (SOLUTIONS OF NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (MCQs (MORE THAN ONE OPTIONS))|8 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section -D SOLUTIONS OF NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS (Long Answer Type Questions )|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE-SECTION -D (SOLUTIONS OF NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)
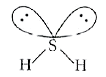
- Explain the non-linear shape of H(2)S and a non-planer shape of PCl(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic c...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the shape of BrF(5).
Text Solution
|
- Structures of molecules of two compounds are given below : (a) Wh...
Text Solution
|
- Why does type or overlap given in the following figure not result in b...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why PCl(5) is trigonal bipyramidal whereas IF(5) is square pyr...
Text Solution
|
- In both water and dJmethyl ether (CH(3) - underset(..)overset(..)(O) -...
Text Solution
|
- Write Lewis structure or the following compounds and show formal charg...
Text Solution
|
- The energy of sigma 2p(z) molecular orbital is greater than pi 2p(x) a...
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of the following processes on the bond order in N(2...
Text Solution
|
- Covalent bonds are directional bonds while ionic bonds are non-directi...
Text Solution
|
- Water molecule has bent structure whereas carbon dioxide molecule is l...
Text Solution
|
- Ethyne molecule is linear
Text Solution
|
- Whal is an ionic bond ? With two suitable examples explain the differe...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following bonds in order of increasing ionic character giv...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why CO(3^(2-) ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis stru...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the hybridization of each carbon in the molecule of organic co...
Text Solution
|
- Group the following as linear and non-linear molecules: H(2) O, HOCl, ...
Text Solution
|
- Elements X, Y and Z have 4, 5 and 7 valence electrons respectively, ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonating structure of (A) Ozone molecule (B) Nitrate ion
Text Solution
|