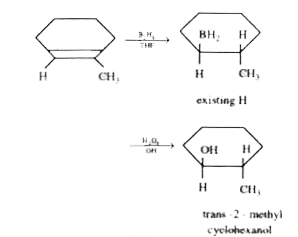
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROCARBONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE SHEET ( LEVEL-II (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS(PASSAGE-III))))|3 VideosHYDROCARBONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE SHEET ( LEVEL-II (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS(PASSAGE-IV))))|3 VideosHYDROCARBONS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE SHEET ( LEVEL-II (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS(PASSAGE-I))))|3 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS|35 VideosHYDROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems