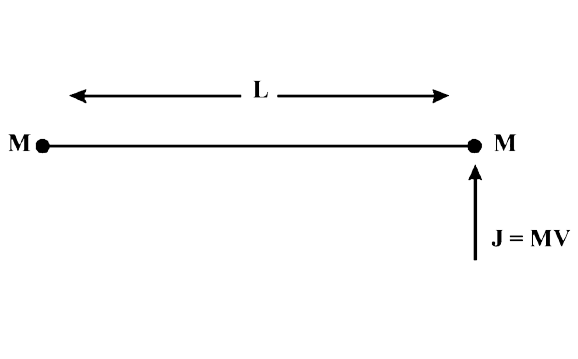
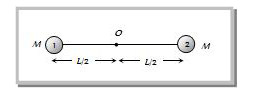
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
ERRORLESS |Exercise Practice Problems (Problems based on centre of mass)|12 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
ERRORLESS |Exercise Practice Problems (Problems based on angular displacement, velocity and acceleration)|16 VideosNEWTONS LAWS OF MOTION
ERRORLESS |Exercise Self Evaluation Test|16 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
ERRORLESS |Exercise simple Harmonic Motion|21 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ERRORLESS -ROTATIONAL MOTION-Practice Problems (Problems based on motion of connected mass)
- Consider a body, shown in figure, consisting of two identical balls, e...
Text Solution
|
- A mass M is supported by a massless string wound round a uniform cylin...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of radius R and mass M can rotate on a smooth axis pass...
Text Solution
|
- A massless rope is wrapped several times on a disc of mass M and radiu...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass M and of radius R is fixed on a frictionless ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass M and of radius R is fixed on a frictionless ...
Text Solution
|
- In the above problem the angular velocity of the system after the part...
Text Solution
|
- A metre scale is suspended vertically from a horizontal axis passing t...
Text Solution
|
- A disc is made to oscillate about a horizontal axis passing through mi...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cube of side l is made to oscillate about a horizontal axis pa...
Text Solution
|
- The string of a simple pendulum replaced by a uniform rod of length L ...
Text Solution
|