A heating element of resistance r is fitted inside an adiabatic cylinder which carries a frictionless piston of mass in and cross-section A as shown in diagram. The cylinder contains one mole of an ideal diatomic gas. The current flows through the element such that the temperature rises with time `t` as `DeltaT = alphat + 1/2beta t^2` (`alpha` and `beta` are constants), while pressure remains constant. The atmospheric pressure above the piston is `P_0`. Then
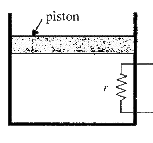
the rate of increase in internal energy is `5/2 R (alpha + beta t)`
the current flowing in the element is `sqrt(5/(2r)(alpha +betat))`
the piston moves upwards with constant acceleration
the piston moves upwards with constant speed