Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MAXIMUM PUBLICATION-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS-EXERCISE
- Elasticity is an internal property of matter. Fluids possess volume el...
Text Solution
|
- Elasticity is the property of a body by which it regains its original ...
Text Solution
|
- Elasticity is the property of a body by which it regains its original ...
Text Solution
|
- When the pressure on a shpere s increased by 80 atmospheres, its volum...
Text Solution
|
- When a mass is suspended on a metallic wire, the length of the wire in...
Text Solution
|
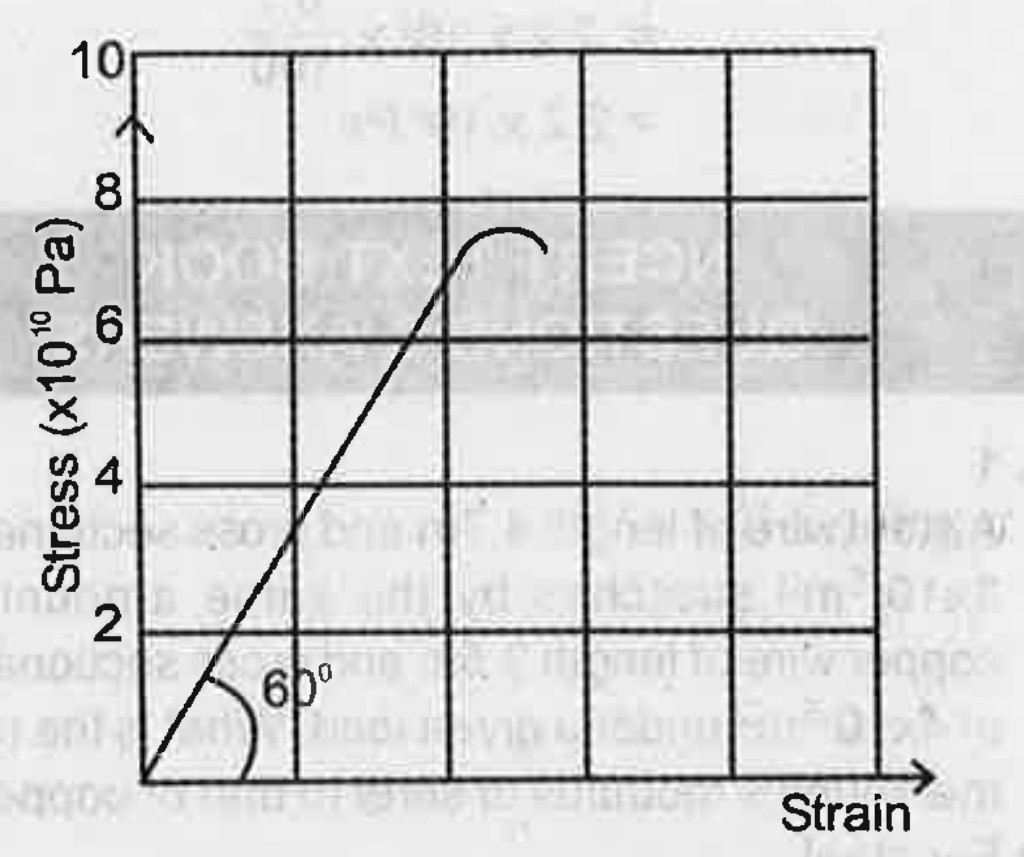
- Draw the stress-strain graph of a loading wire. Mark the following poi...
Text Solution
|
- When a mass is suspended on a metallic wire, the length of the wire in...
Text Solution
|
- When a wire is stretched with a very large force it breaks. Represent ...
Text Solution
|
- When a wire is stretched with a very large force it breaks. Discuss th...
Text Solution
|
- When a wire is stretched with a very large force it breaks. State Hook...
Text Solution
|
- Elasticity is the property of a body by which it regains its original ...
Text Solution
|
- Hooke's law states that stress alpha strain. What is the necessary con...
Text Solution
|
- Stress - Strain graph of two materials is shown below: State the law w...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following
Text Solution
|
- The graph below shows how the force applied to a metal wire is related...
Text Solution
|
- Name the law relating stress and strain.
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the stress developed in a metal wire when it is strained by ...
Text Solution
|
- Elasticity is the property of a body by which it regains its original ...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid body is a body with a perfectly unchanging shape under the inf...
Text Solution
|
- Young's moduli of three materials are given in the above table. Select...
Text Solution
|