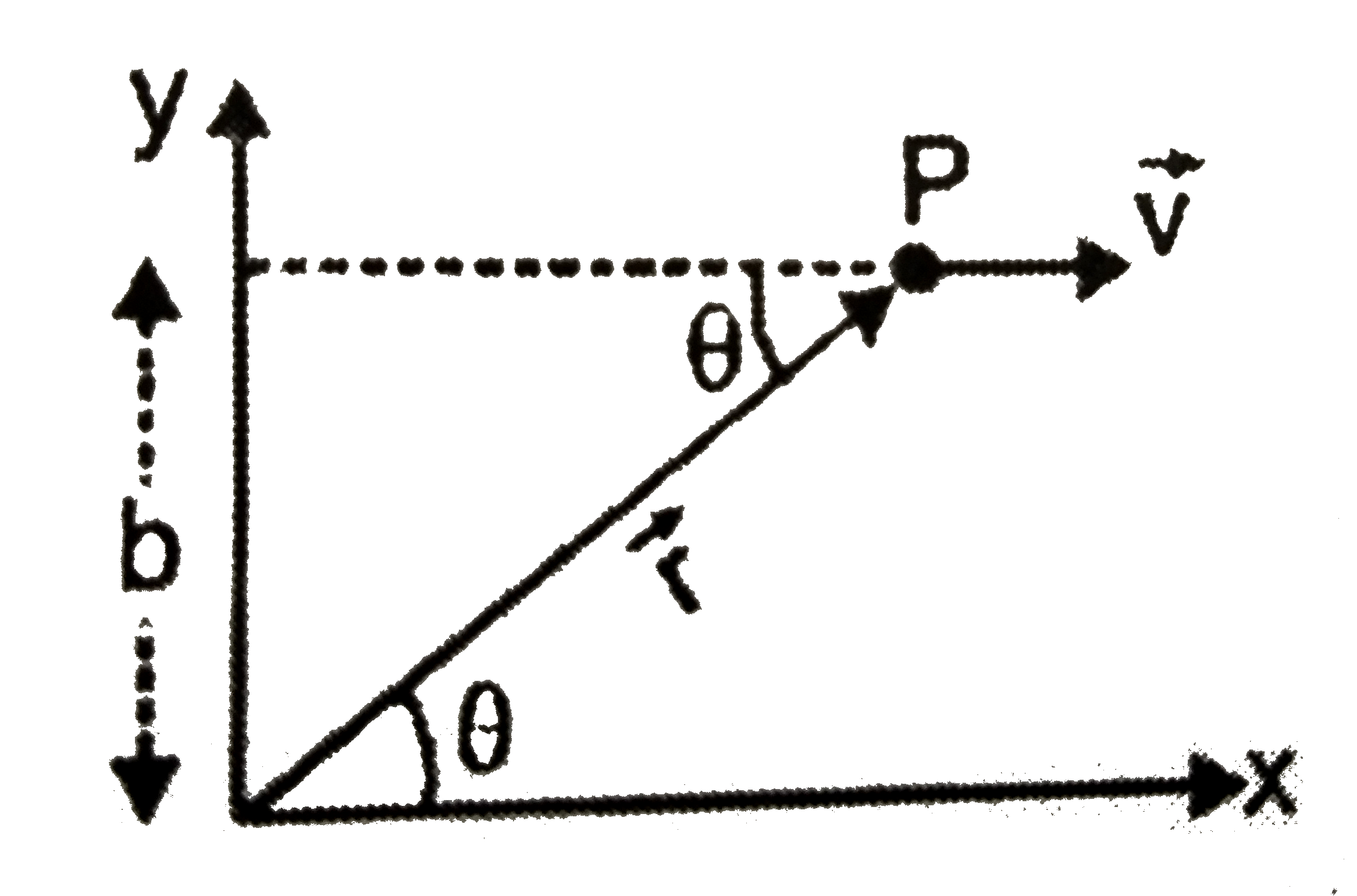
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A particle moving parallel to x-axis as shown in fig. such that at all...
Text Solution
|
- A particle mass parallel to x-axis with constant velocity v as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moving parallel to x-axis as shown in fig. such that at all...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with constant speed v along the line y = a in pos...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving along a straight line parallel to x-axis with con...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves parallel to X-axis as shown in the figure such that a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is going parallel to x - axis with constant speed V at a di...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with a contant velocity along a line parallel to ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is going parallel to x-axis with constant speed V at a dist...
Text Solution
|