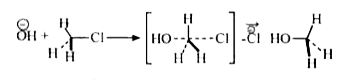Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNSTAR PUBLICATION-ANNUAL EXAM QUESTION PAPER MARCH - 2017-PART - D
- write any two differences between lyophilic and lyophobic colloids .
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
Text Solution
|
- How does entropy change for adsorption?
Text Solution
|
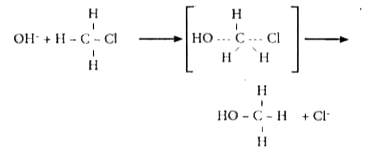
- Write SN^(2) mechanism of the conversion of methyl chloride to methyl ...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones towards nucleophill...
Text Solution
|
- What is asymmetric carbon atom.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Kolbe's reaction with equation.
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to ethene...
Text Solution
|
- How benzene is converted into benzaldehyde by Gatterman-Koch reaction.
Text Solution
|
- Complete and name the following reaction.
Text Solution
|
- What is the effect of electron withdrawing group on the acidity of car...
Text Solution
|
- How aniline is prepared by Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction? Gi...
Text Solution
|
- i) Write IUPAC name of CH(3)CH(2)NH(2). ii) Arrange the following am...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following equation. C(6)H(5)NH(2)+NaNO(2)+2HCl overset(...
Text Solution
|
- Write Haworth structure for maltose.
Text Solution
|
- Give an example for i) Globular proteins. ii) Naturally occurring ...
Text Solution
|
- Name the nucleic acid which is responsible for genetic inform...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the preparation of Buna-N with equation.
Text Solution
|
- Name the monomer present in the following polymer i) Poly vinyl chlo...
Text Solution
|
- Give an example for biodegradable polymer.
Text Solution
|