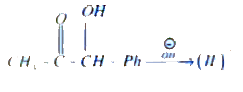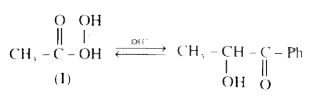A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (LEVEL-II) LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE QUESTIONS)|5 VideosISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (LEVEL-II) MATRIX MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS)|2 VideosISOMERISM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (LEVEL-I) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)|20 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (LEVEL -II PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED) (Integer Type Questions))|8 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCISE - 3 (RECENT AIPMT/NEET QUESTIONS)|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-ISOMERISM -PRACTICE SHEET (EXERCISE-I (LEVEL-II) STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS)
- Which of the following statements is right
Text Solution
|
- Tautomer in following is Diad system :
Text Solution
|
- What statement is correct for Keto-enol tautomerism ?
Text Solution
|
- Tautomer of following compound is :
Text Solution
|
- Tautomerism is exhibited by X number of compounds among the following....
Text Solution
|
- Maximum enolisation takes place in :
Text Solution
|
- Tautomerism exhibited by
Text Solution
|
- Tautomers possess
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are incorrect about keto-enol tautomerism?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the fillowing pairs cannot exist in between two structural is...
Text Solution
|
- The percentage of enol content in the following is in the order I) C...
Text Solution
|
- (I) isomerizes to (II) on addition on small amount of base structure o...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following can tautomerise.
Text Solution
|
- Decreasing order of enol content of the following compound in liquid p...
Text Solution
|
- Metamerism is exhibited by
Text Solution
|
- There exists the tautomeric forms Which are correct
Text Solution
|
- Chain isomer of cyclobutene is
Text Solution
|
- Minimum number of carbon required to exhibit chain isomerism
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following cases enol content will be higher than the k...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are functional isomers of methyl ethanoate ?
Text Solution
|