Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
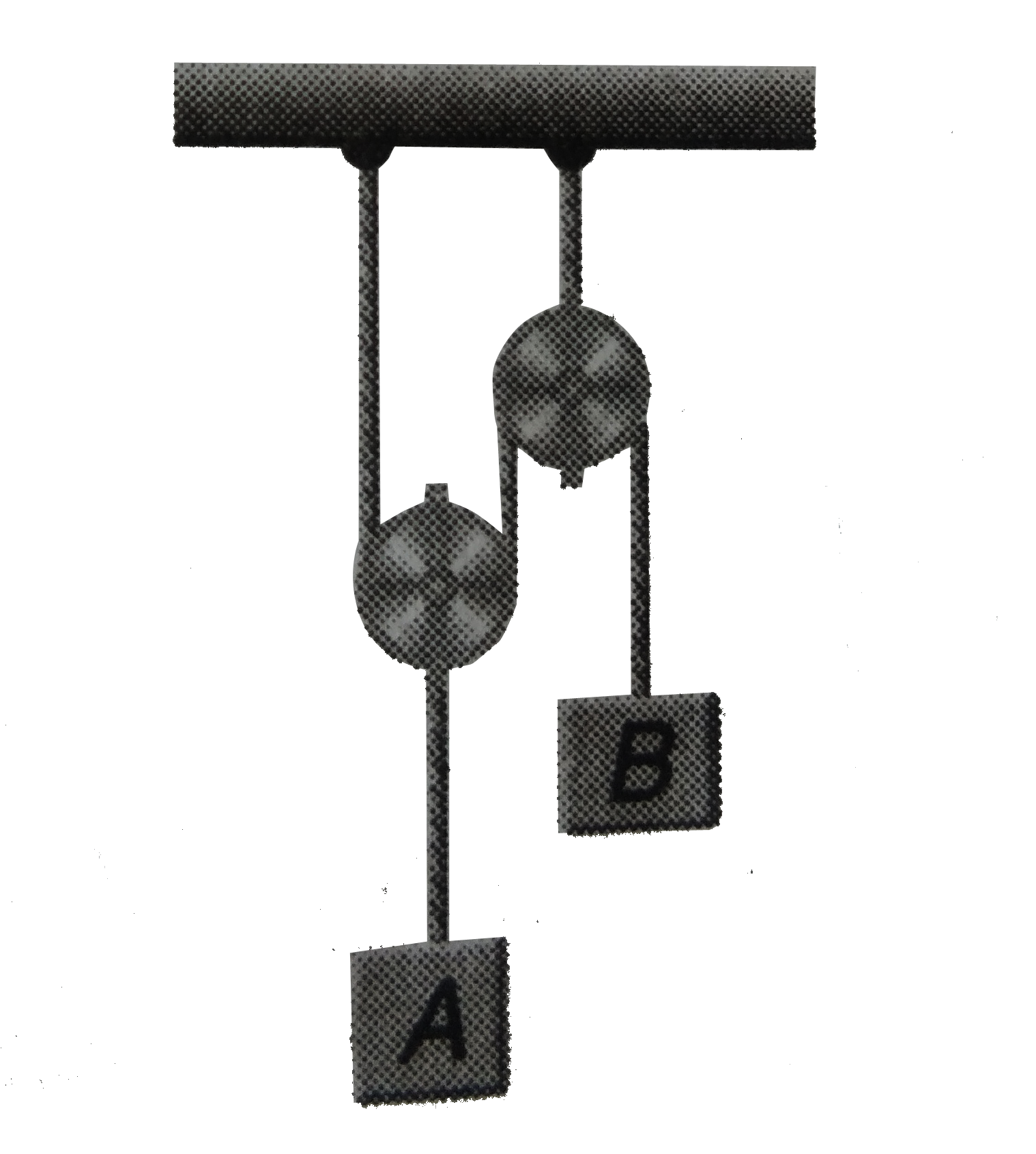
- Block A has a weight of 3000 N and block B has a weight of 500 N. Dete...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the acceleration of the 5 kg block A . Neglect the mass of t...
Text Solution
|
- Block A has a weight of 3000 N and block B has a weight of 500 N. Dete...
Text Solution
|
- The system is released from rest with the spring initally stretched 75...
Text Solution
|
- Block A has a weight of 3000 N and block B has a weight of 50 N . Coef...
Text Solution
|
- Block A has a mass of 5kg and is placed on top of a smooth triangular ...
Text Solution
|
- Block A of weight 500 N and block B of weight 700 N are connected by r...
Text Solution
|
- Block A has a weight of 300 N and block B has weight 50 N. Calculate t...
Text Solution
|
- Block A weights 4 N and block B weights 8 N. The coefficient of kineti...
Text Solution
|
 .
.