A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 1 Subjective|48 VideosTHERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Single Correct|12 VideosTHERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 1 Assertion And Reason|10 VideosTHERMOMETRY THERMAL EXPANSION AND KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical entrance gallary|30 VideosUNIT AND DIMENSIONS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion And Reason|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-THERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-Level 1 Objective
- The average velocity of molecules of a gas of molecular weight (M) at ...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles have velocities 1, 0,2, and 3 m//s. The root mean squar...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27 ^@ C to 927^(@)C....
Text Solution
|
- In case of hydrogen and oxygen at (NTP), which of the following is the...
Text Solution
|
- The average kinetic energy of the molecules of an ideal gas at 10 ^@ C...
Text Solution
|
- A polyatomic gas with (n) degress of freedom has a mean energy per mol...
Text Solution
|
- In a process, the pressure of a gas remains constant. If the temperatu...
Text Solution
|
- A steel rod of length 1 m is heated from 25^@ "to" 75^@ C keeping its ...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of linear expansion of steel and brass are 11 xx 10^-6...
Text Solution
|
- The expansion of an ideal gas of mass (m) at a constant pressure (p) i...
Text Solution
|
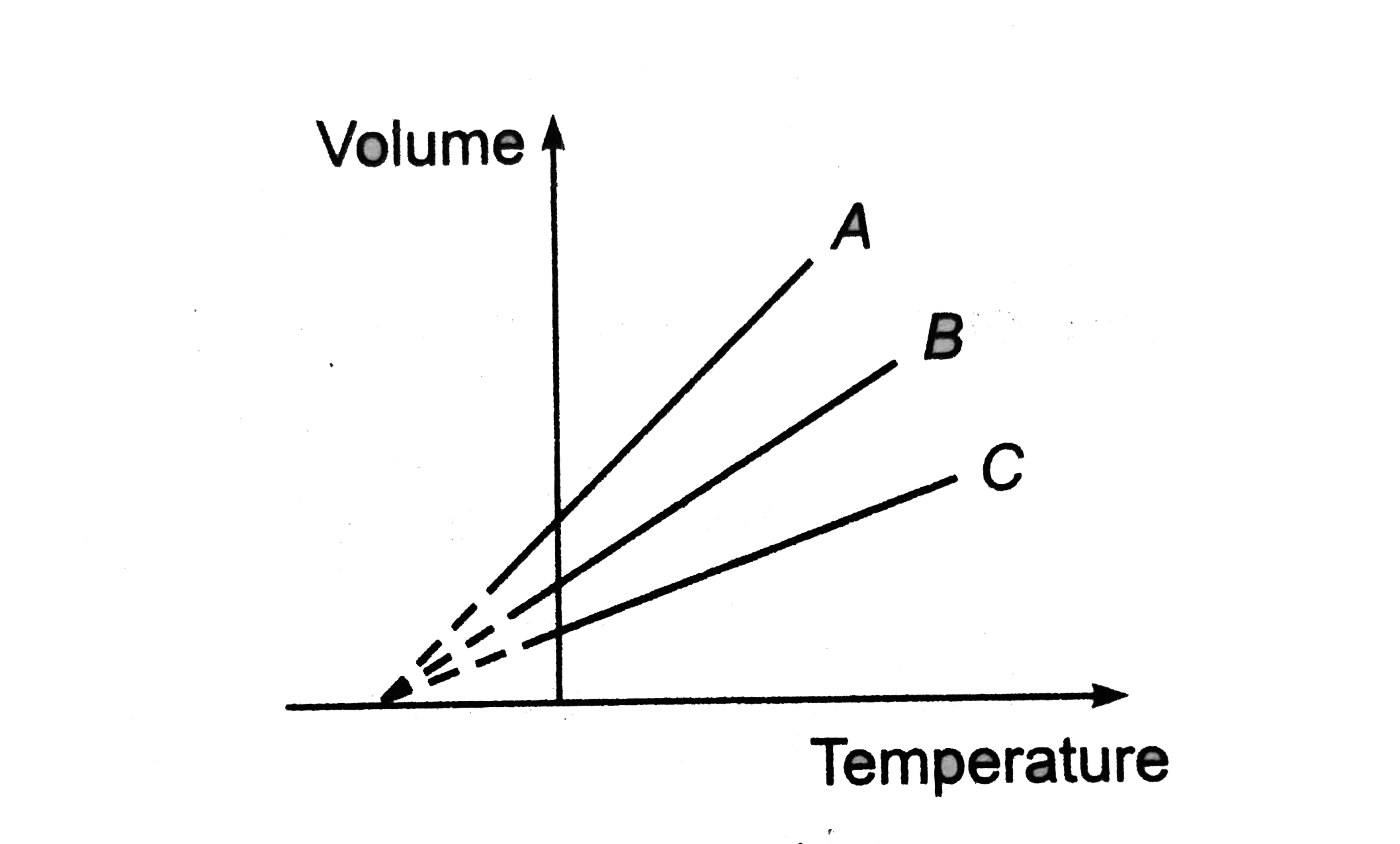 .
.