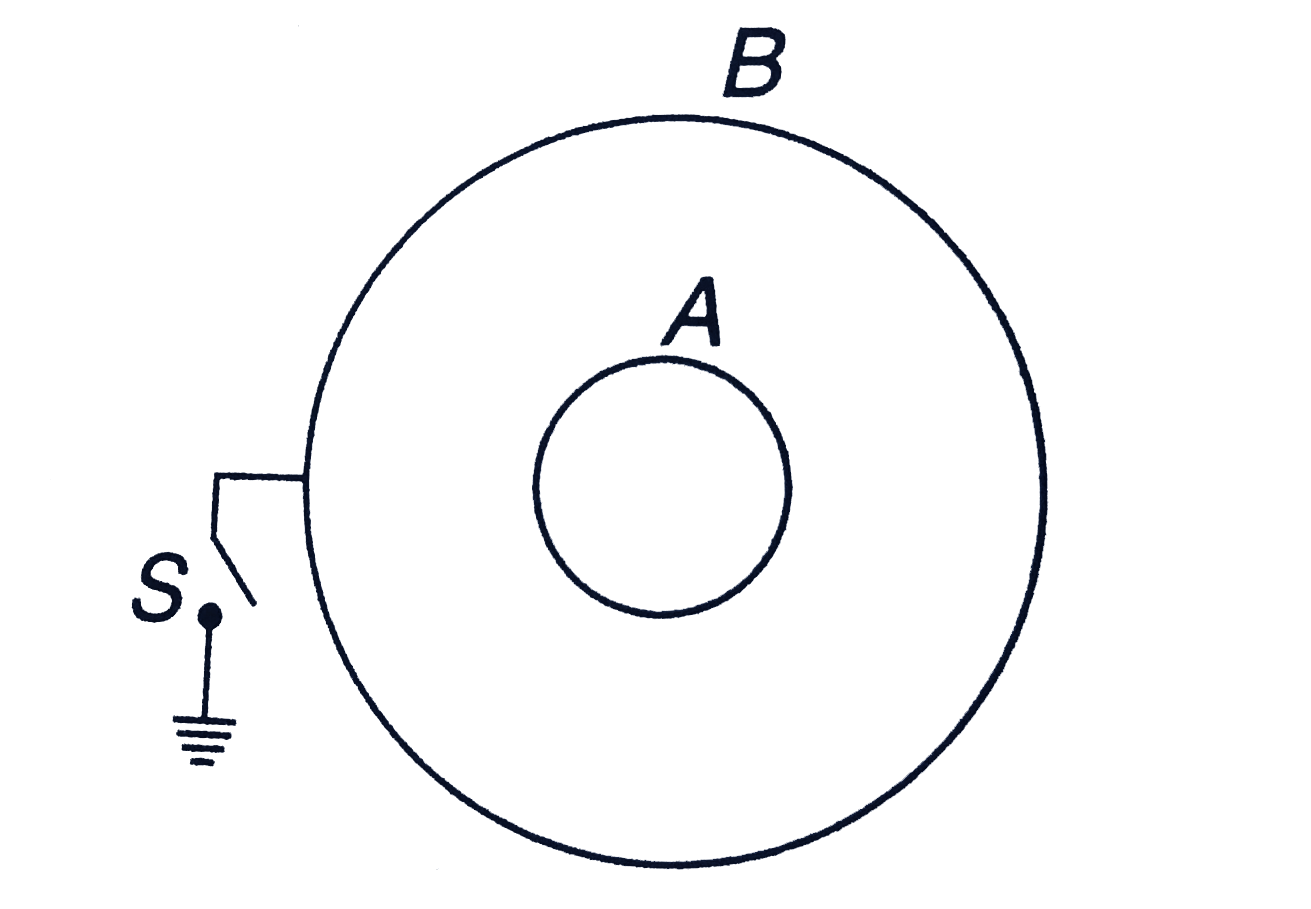
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Example Type 8|3 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Single Correct|94 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Example Type 5|5 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITORS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise (C) Chapter exercises|50 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise All Questions|135 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-Example Type 6
- A point charge q is placed at the centre of a cube. What is the flux l...
Text Solution
|
- Three conducting spherical shells have charges q,-2q and 3q as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two conducting thin concentric shells of radi r and 3r. T...
Text Solution
|
- Initially the spheres A and B are at potentials VA and VB. Find the po...
Text Solution
|