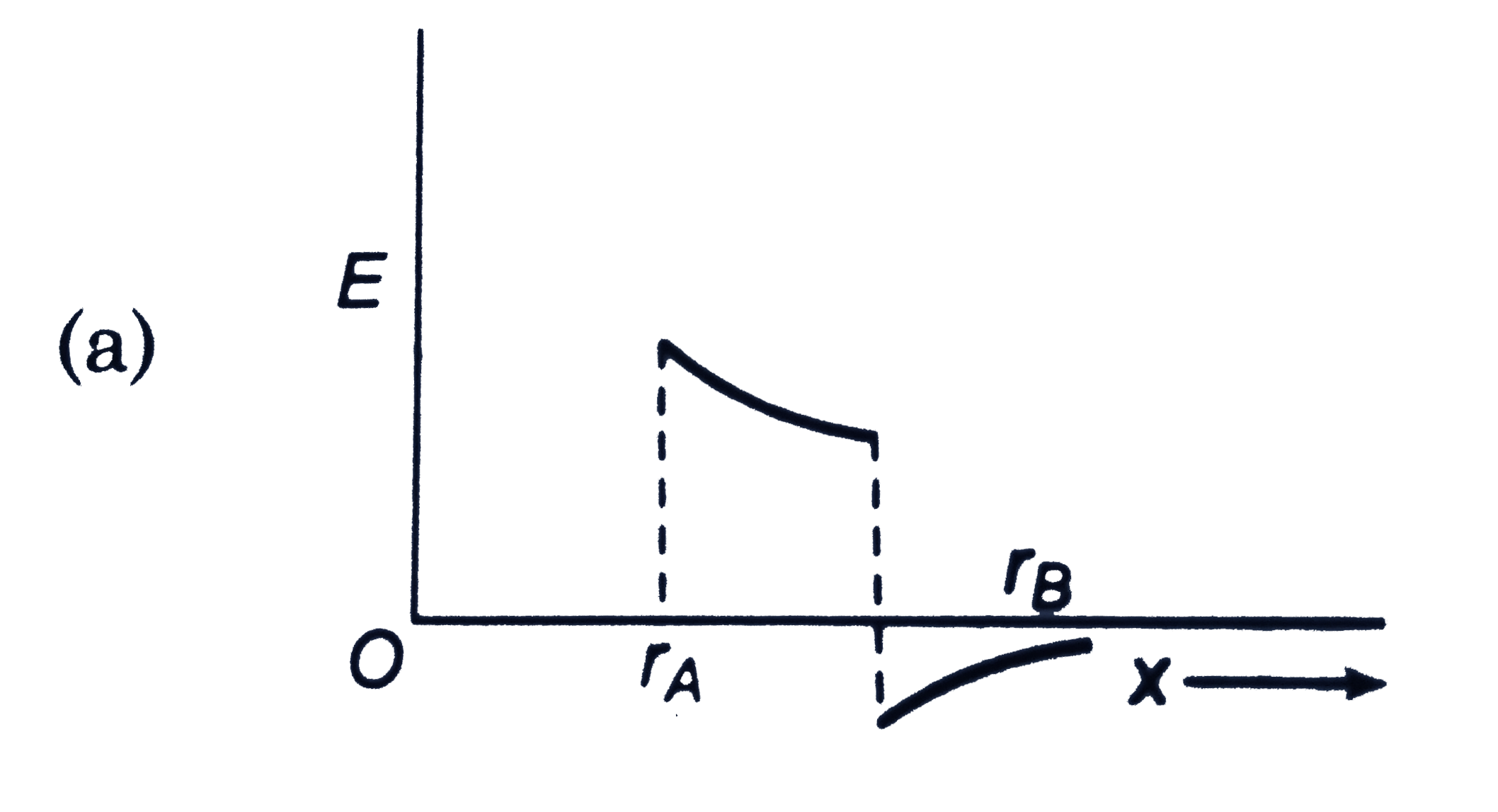
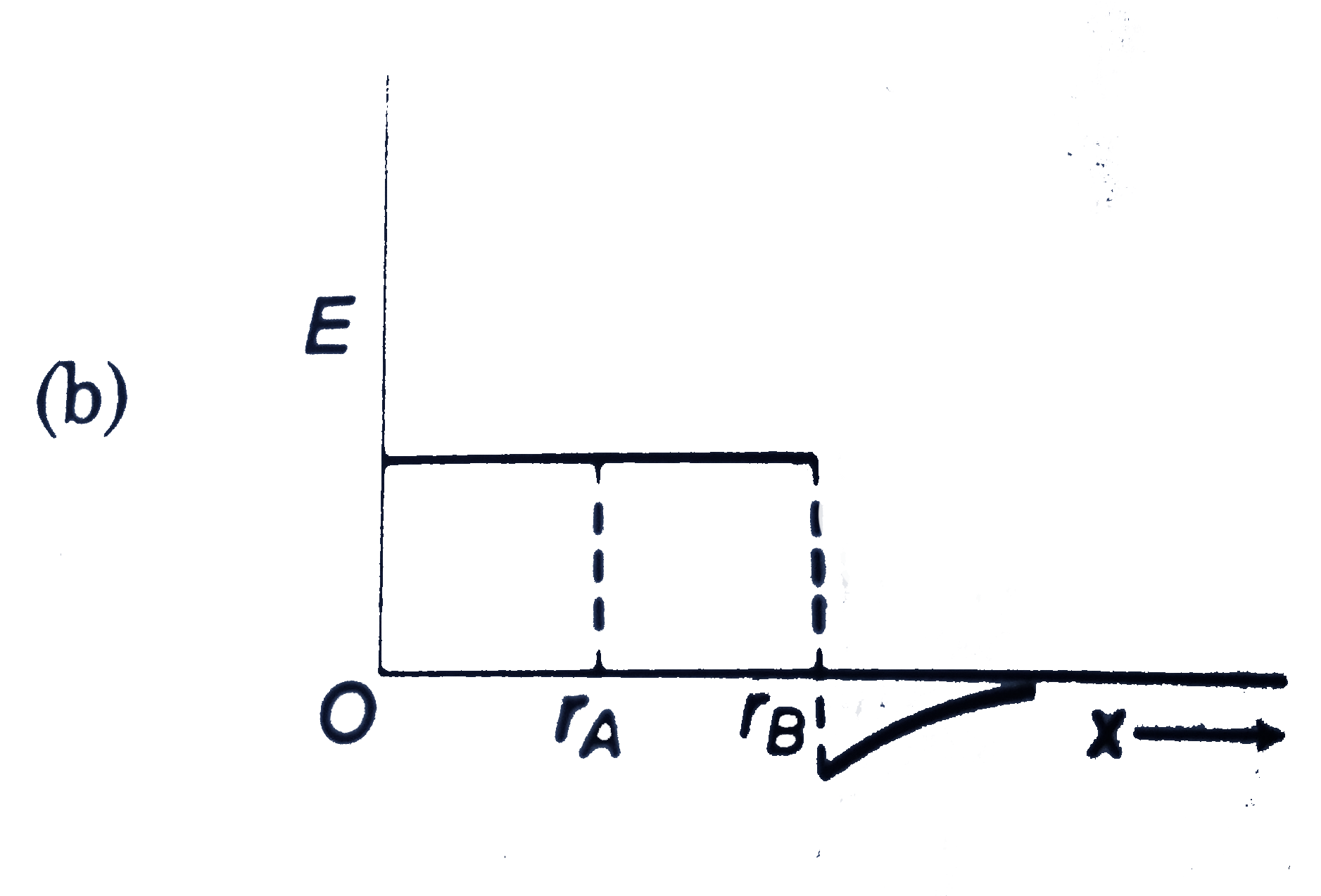
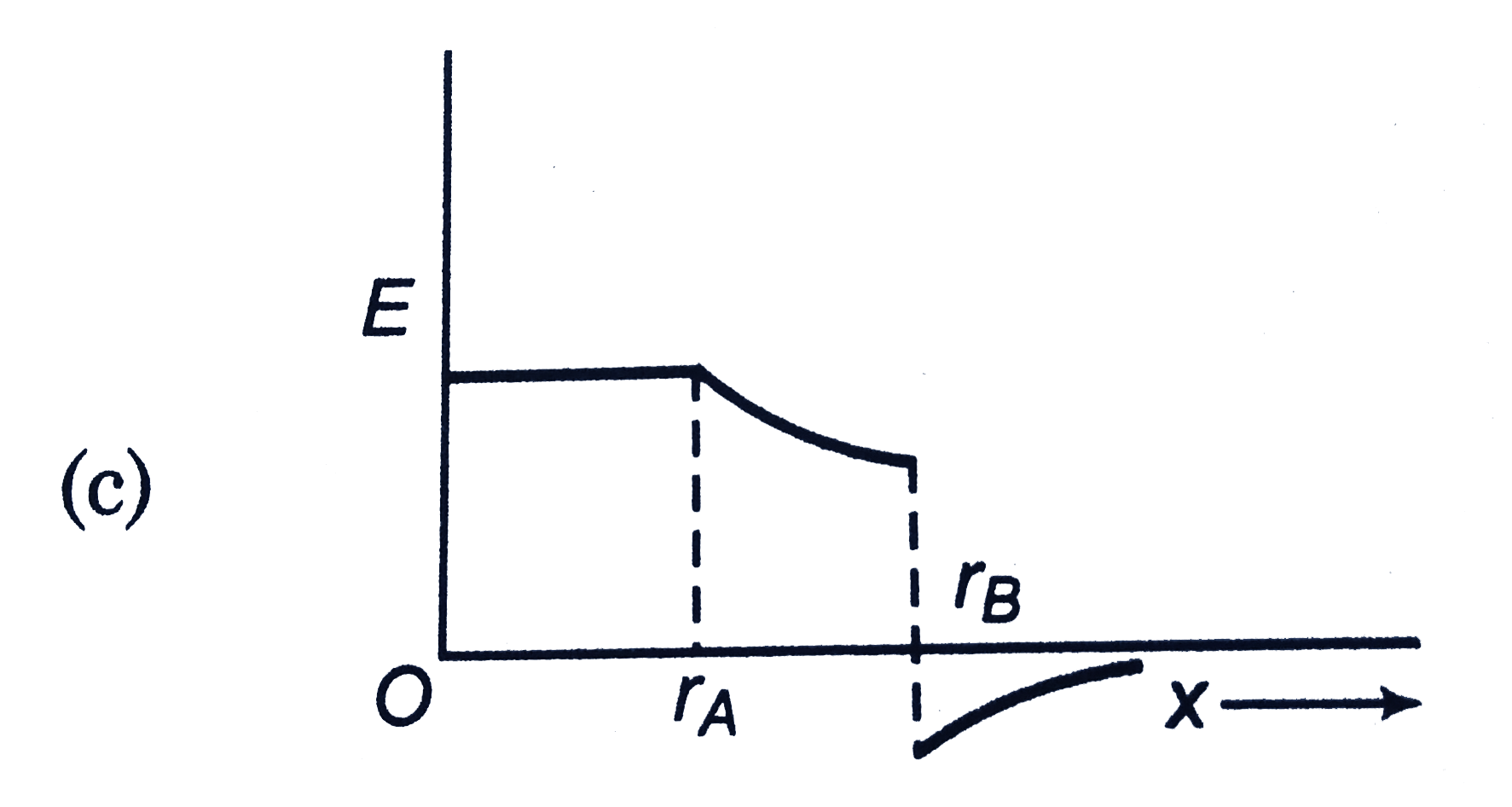
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 24.1|4 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 24.2|9 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Example Type 8|3 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITORS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise (C) Chapter exercises|50 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise All Questions|135 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-Level 2 Single Correct
- There are two uncharged identicasl metallic spheres 1 and 2 of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a closed surface which intersects a conducting sphere. If...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric coducting thin spherical shells A and B having radii rA...
Text Solution
|
- The electric potential at a point (x,y) in the x-y plane is given by V...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric shells have radii R and 2R charges qA and qB and potent...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2 kg charge 1 mC is projected vertially with veloc...
Text Solution
|
- At a distance of 5 cm and 10 cm outward from the surface of a uniforml...
Text Solution
|
- Three charged particle sare in equilibrium under their electrostatic f...
Text Solution
|
- Charges Q1 and Q2 lie inside and outside, respectively, of a closed su...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a sphere. Mark the corre...
Text Solution
|
- Mark correct options
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric spherical shells have charges +q and -q as shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- A rod is hinged (free to rotate) ast its centre O as shown in figue. T...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges +Q each are fixed at points C and D. Line AB is the bisect...
Text Solution
|
- There are two concentric spherical shell of radii r and 2r. Initially,...
Text Solution
|
- There are two concentric spherical shell of radii r and 2r. Initially,...
Text Solution
|
- There are two concentric spherical shell of radii r and 2r. Initially,...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of charges of radius R carries a positive charge whose volume...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of charges of radius R carries a positive charge whose volume...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of charges of radius R carries a positive charge whose volume...
Text Solution
|