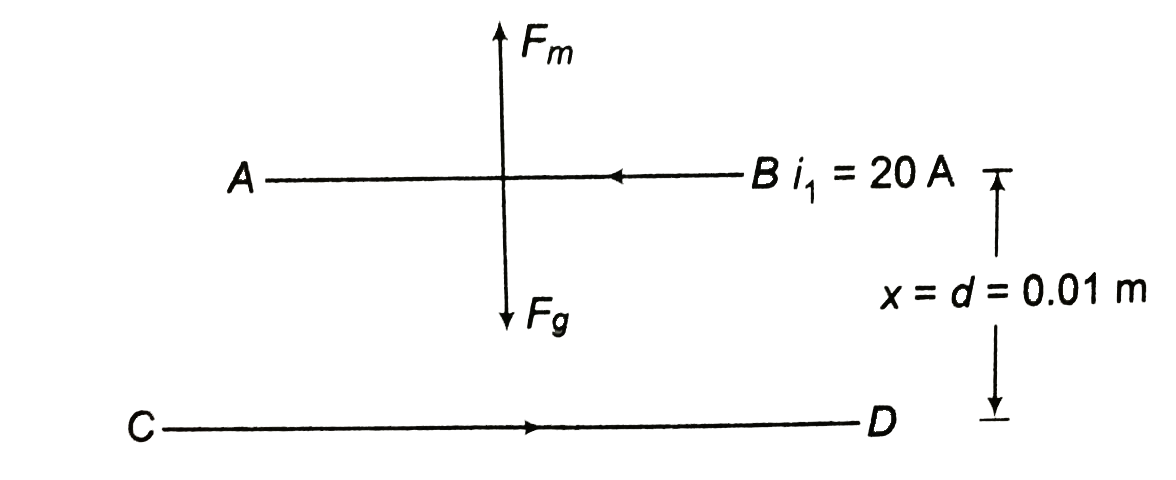
Let `m` be the mass per unit length of wire `AB`. At as height `x` above the wire `CD`, magnetic force per unit length on wire `AB` will be given by
`F_m=mu_0/(2pi) (i_1i_2)/x` (upwards) ……….i
Weight per unit length of wire AB is
`F_g=mg` (downwards)
Here m=mass per unit length of wire `AB`
At `x=d`, wire is in equilibrium i.e.
`F_m=F_g`
or `m_0/(2pi) (i_1i_2)/d=mg`
or `mu_0/(2pi) (i_1i_2)/d^2=(mg)/d`.........ii
When `AB` is depressed `x` decrease `x` decreases therefore, `F_m` will increase, while `F_g` remains the same. Change in magnetic force will become the net restoring force,Let `AB` is displaced by `dx` downwards.
Differentiating eqn i w.r.t x, we get
`dF_m=mu_0/(2pi)(i_1i_2)/x^2.dx`.........iii
i.e. restoring force `F=dF_mprop-dx`
hence the motion of wire is simple harmonic.
From eqn ii and iii we can write
`dF_m=((mg)/d).dx` `[:'x=d`]
:. Acceleration of wire `a=-(g/d).dx`
hence, period of oscillation
`T=2pisqrt((|"displacement"|)/(|"acceleration"|))=2pisqrt(|(dx)/a|)`
or `T=2pisqrt(d/g)=2pisqrt(0.01/9.8)`
or `T=0.2s`