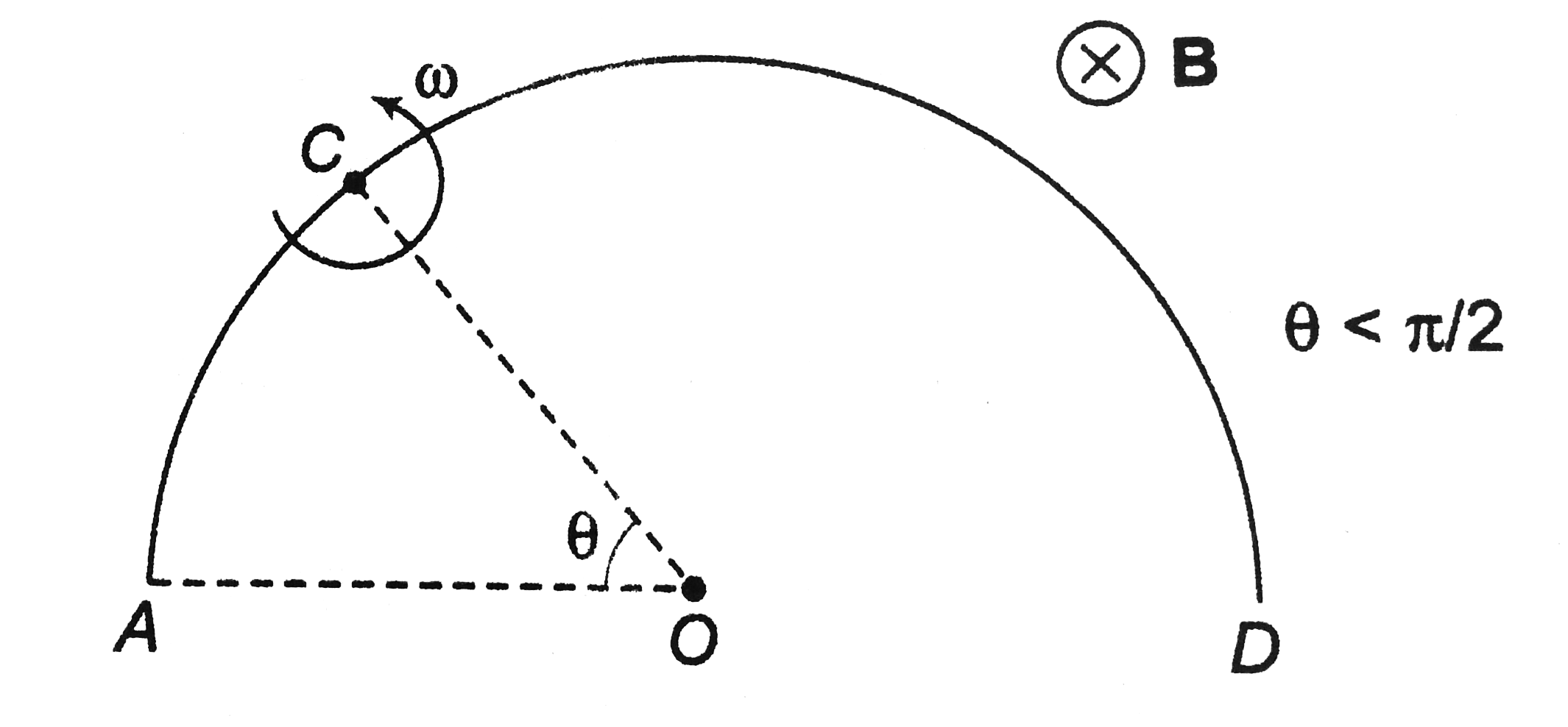
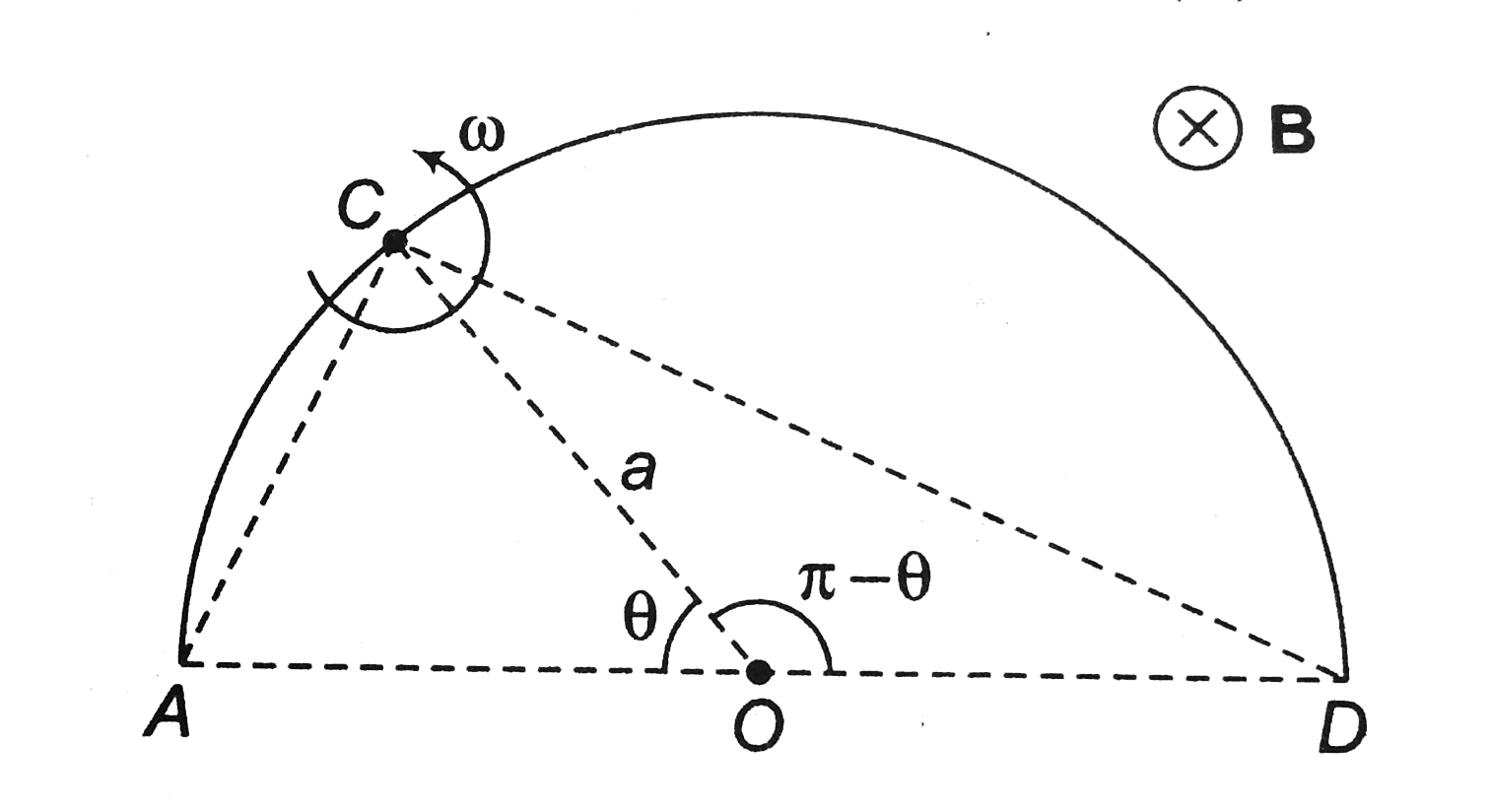
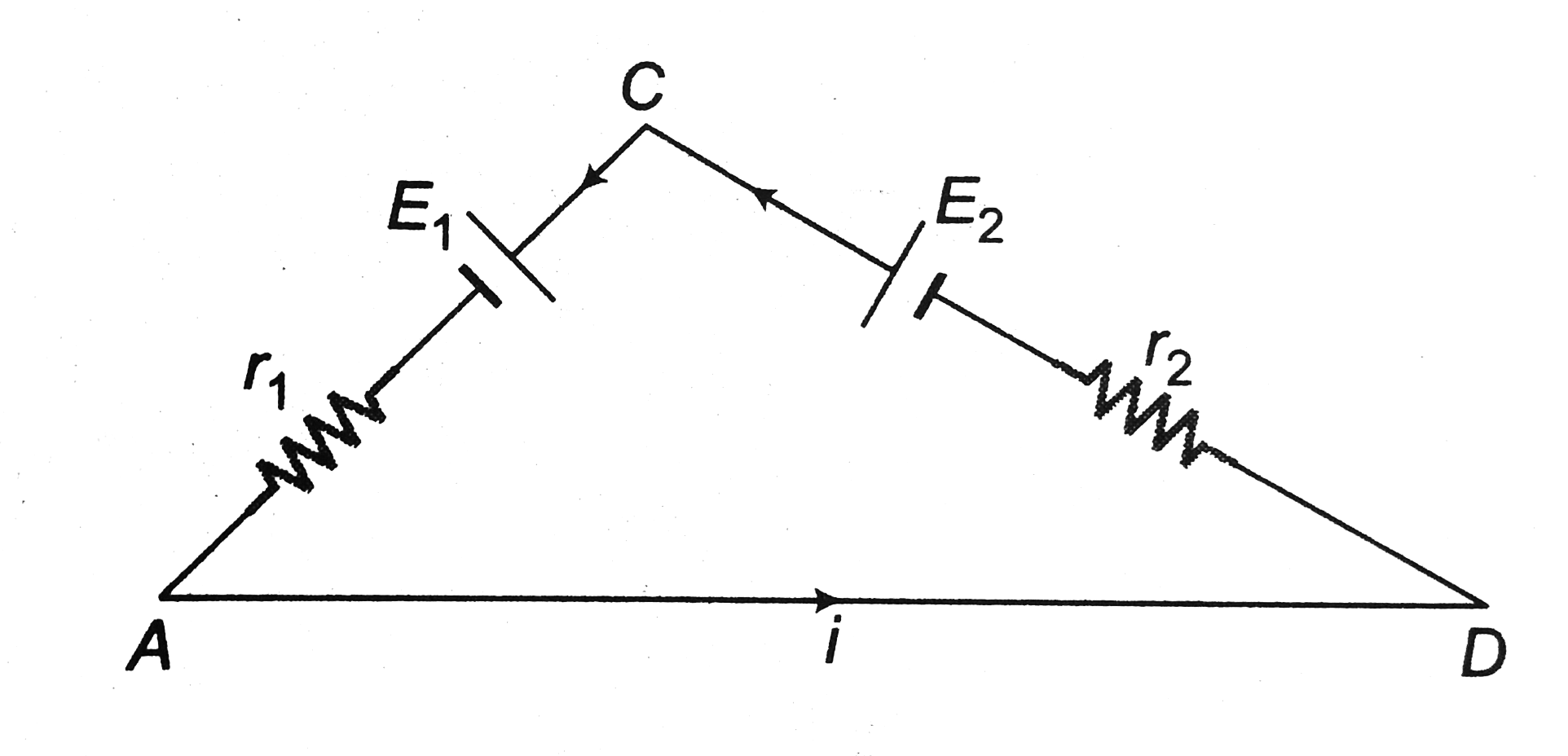
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 27.1|8 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 27.2|4 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Example Type 6|3 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|97 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Sec C|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Miscellaneous Examples
- A sensitive electronic device of resistance 175Omega is to be connecte...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod shown in figure of mass m and length l moves on two f...
Text Solution
|
- A wire loop enclosing as semicircle of radius R is located on the boud...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform wire of resistance per unit length lambda is bent into semi...
Text Solution
|
- A battery of emf E and of negligible internal resistance is connected ...
Text Solution
|