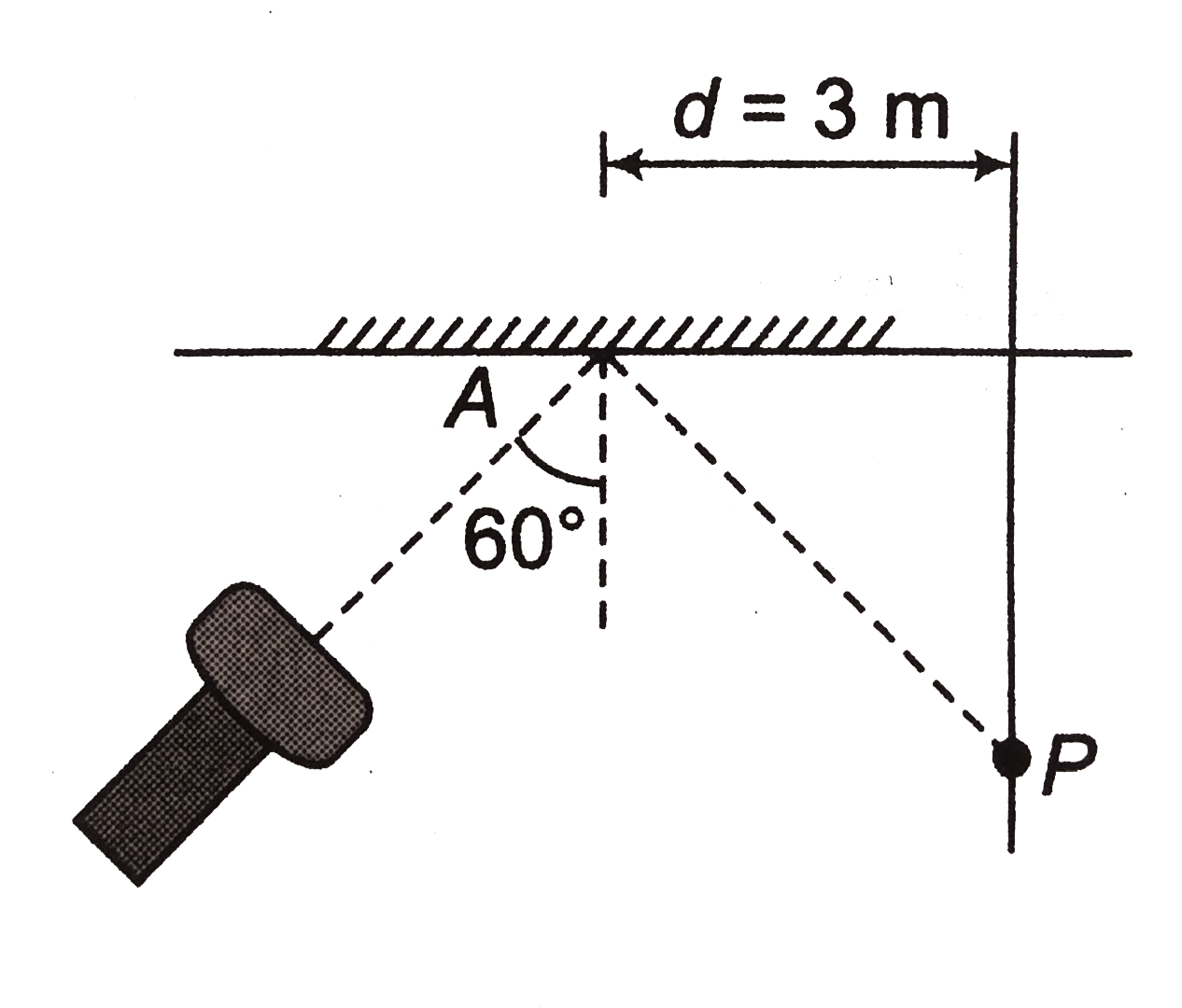
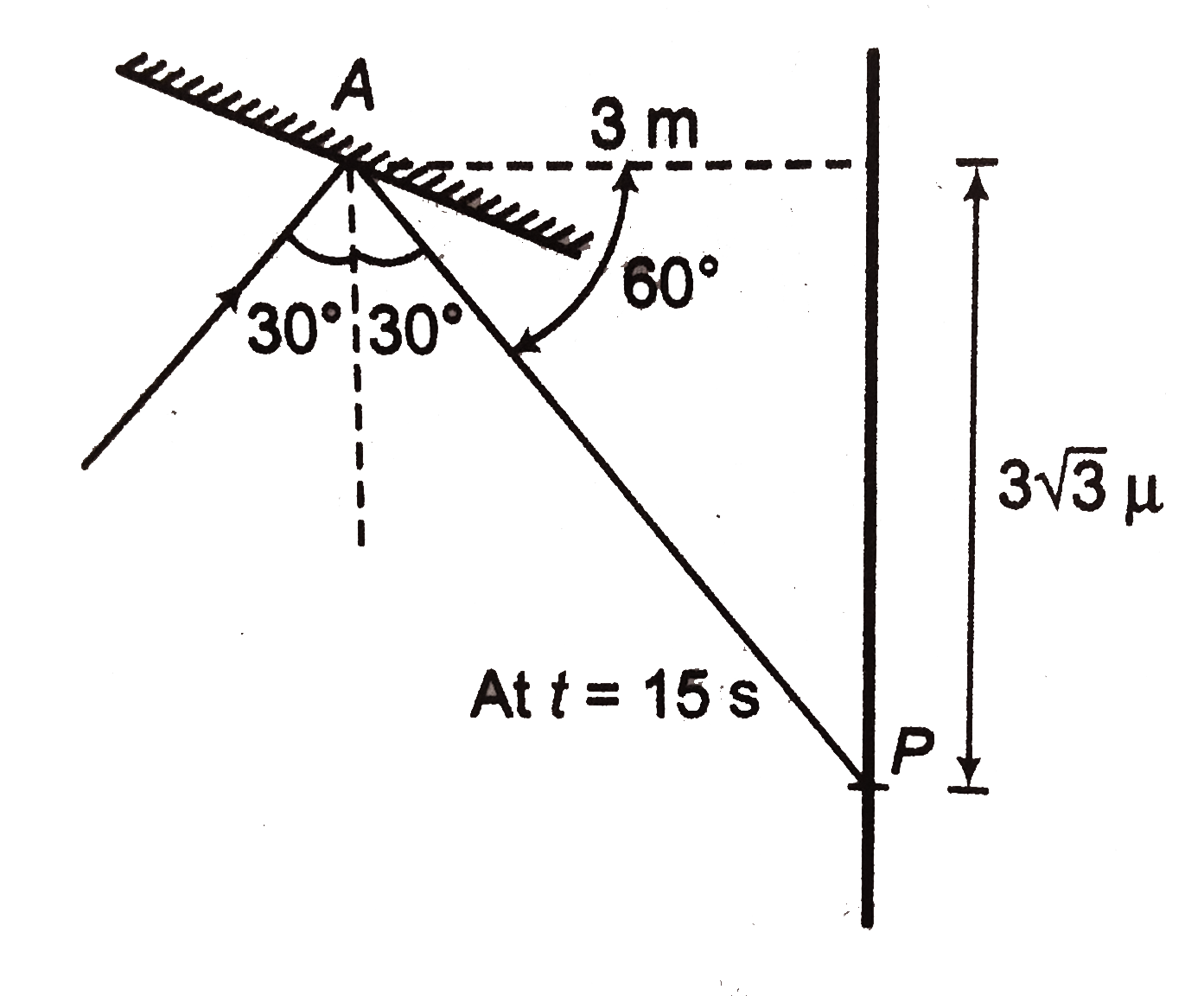
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-REFLECTION OF LIGHT-Subjective
- A point source of light S is placed at a distance 10 cm in front of th...
Text Solution
|
- Concave mirror forms the real image of a point source lying on the opt...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light S is placed on the major optical axis of the c...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon is moving upwards with a speed of 20 m//s. When it is at a h...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror and a concave mirror are arranged as shown in figure an...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a torch producting a straight light beam falling on a pla...
Text Solution
|
- A thief is running away in a car with velocity of 20 m//s. A police je...
Text Solution
|
- A ball swings back and forth in front of a concave mirror. The motion ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that a parallel bundle of light rays parallel to the x-axis and i...
Text Solution
|