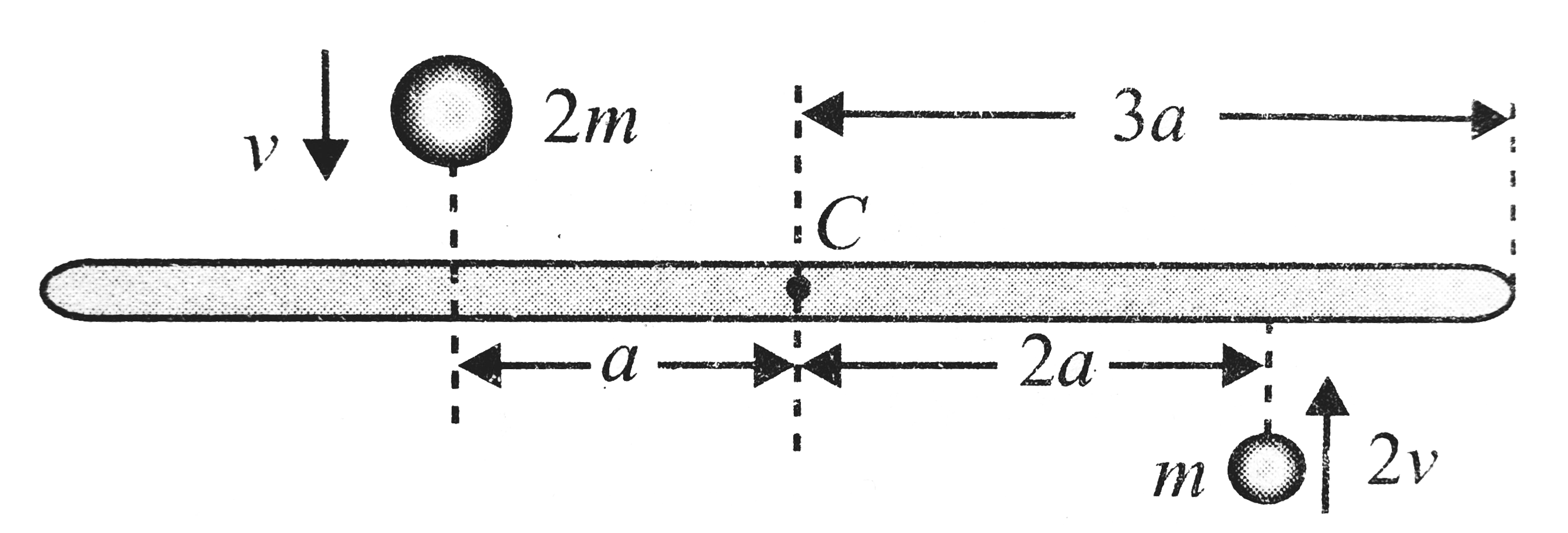
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type Questions|40 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Matrix Matching Type Questions|16 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise A Only One Option is Correct|86 VideosROTATIONAL MECHANICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Questions|2 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise More than One Option is Correct|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ROTATIONAL MOTION-More than one option is correct
- Which of the following statement (s) is / are correct for a spherical ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a circle of radius r with angular velocity omega. ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is travelling with a constant velocity v=v(0)hati...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct option: A spool of wire rests on a horizontal sur...
Text Solution
|
- In the above problem, direction of friction force is
Text Solution
|
- A constant force F is applied at the top of a ring as shown in figure....
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a thin square plate ABCD of uniform thickness...
Text Solution
|
- In pure rolling, fraction of its total energy associated with rotation...
Text Solution
|
- The end B of the rod AB which makes angle theta with the floor is bein...
Text Solution
|
- A disc can roll wihtout slippingg, without applying any external force...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of radius R rolls on a horizontal ground with linear speed v an...
Text Solution
|
- If a circular concentric hole is made on a disc then about an axis pas...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc is rotating at a constantt speed in a vertical plane ab...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical body of radius R rolls on a horizontal surface with linear...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R pure rolls on a rough surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R is rolled by a force F acting at the topo o...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass M and radius R moves in the x-y plane as shown in the f...
Text Solution
|
- Four particle of mass m each are placed at four corners of a square AB...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces F(1) " and " F(2) are acting on a rod abc as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|