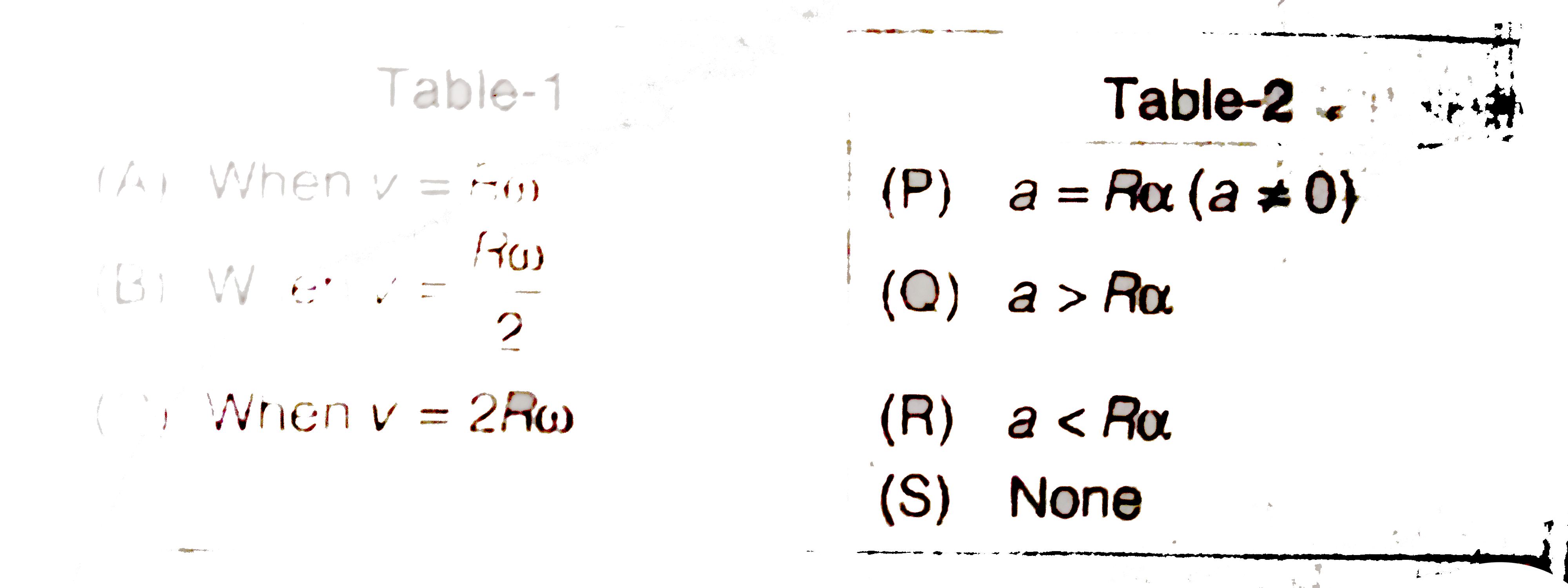Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Integer Type Questions|17 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type Questions|40 VideosROTATIONAL MECHANICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective Questions|2 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise More than One Option is Correct|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ROTATIONAL MOTION-Matrix Matching Type Questions
- Four rods of equal length l and mass m each form a square as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass m and radius R is placed on a rough inclined plane so t...
Text Solution
|
- The particle of mass 1 kg is projected with velocity 20sqrt(2)m/s at 4...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rolls on ground without slipping . Velocity of centre of mass i...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following .
Text Solution
|
- A disc with linear velocity v and angular velocity omega is placed on ...
Text Solution
|
- In net force on a rigid body is zero. Then, match the following table.
Text Solution
|
- If radius of earth is reduced to half without changing its mass,
Text Solution
|
- A semi-circular ring has mass m and radius R as shown in figure. Let I...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere is rotating about an axis as shown in figure. An insect...
Text Solution
|
- In each situation of Table-1, a uniform disc of mass m and radius R ro...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere, a hollow sphere, a solid disc and a hollow cylinder ar...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is lying on a smooth table. An im...
Text Solution
|
- There are two point masses A and B, situated at origin and point (5m,0...
Text Solution
|
- A thin but very large plank of mass 2 m is placed on a horziontal smoo...
Text Solution
|
- Match the following two Tables .
Text Solution
|