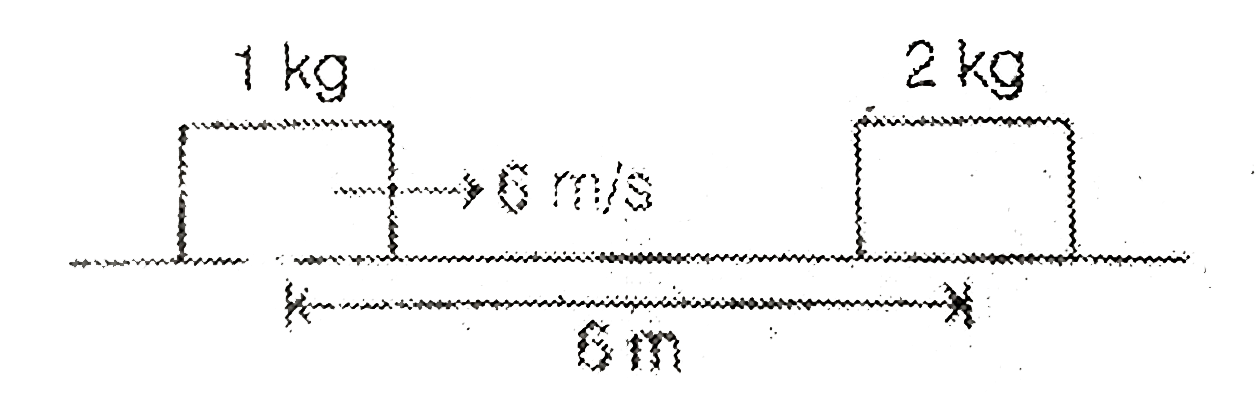A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A block of mass 1 kg is pushed towards another block of mass 2 kg fro...
Text Solution
|
- Initially spring is in its natural length . The block of mass 3 kg in ...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass 2 kg rests on a horizontal surface. Another block B ...
Text Solution
|
- The elevator shown in figure is descending, with an acceleration of 2 ...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown figure both blocks are in equilibrium m=1 kg. a bullet of...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, block of mass 2 kg is very long. Force of frictio...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2 kg is pushed towards a very heavy object moving with...
Text Solution
|
- 2 mass of block 2 kg & 4 kg are attached to a stiffness spring 100 N/m...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement as shown, block A of mass 3 kg moves towards left w...
Text Solution
|