A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
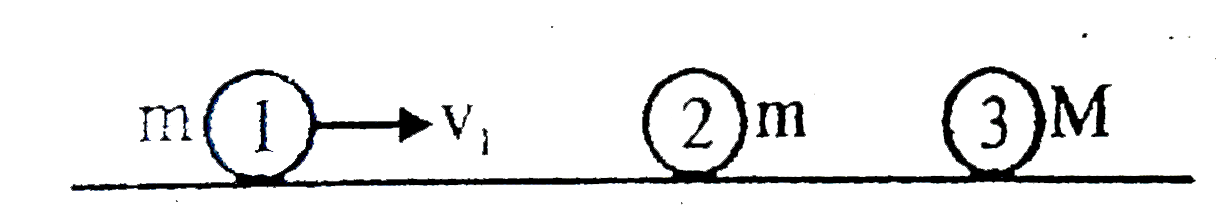
- Two balls marked 1 and 2 of the same mass m and a third ball marked 3 ...
Text Solution
|
- A heavy ball of mass 2M moving with a velocity v(0) collides elastical...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with velocity V, makes a head on elastic colli...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls each of mass 'm' are moving with same velocity v on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls marked 1 and 2 of the same mass m and a third ball marked 3 ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m moving with a velocity v undergoes an oblique elastic...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls each of mass 'm' are moving with same velocity v on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 4 kg moving on a smooth horizontal surface makes an ela...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m= 1 kg falling vertically with a velocity v(0) = 2 m/s...
Text Solution
|