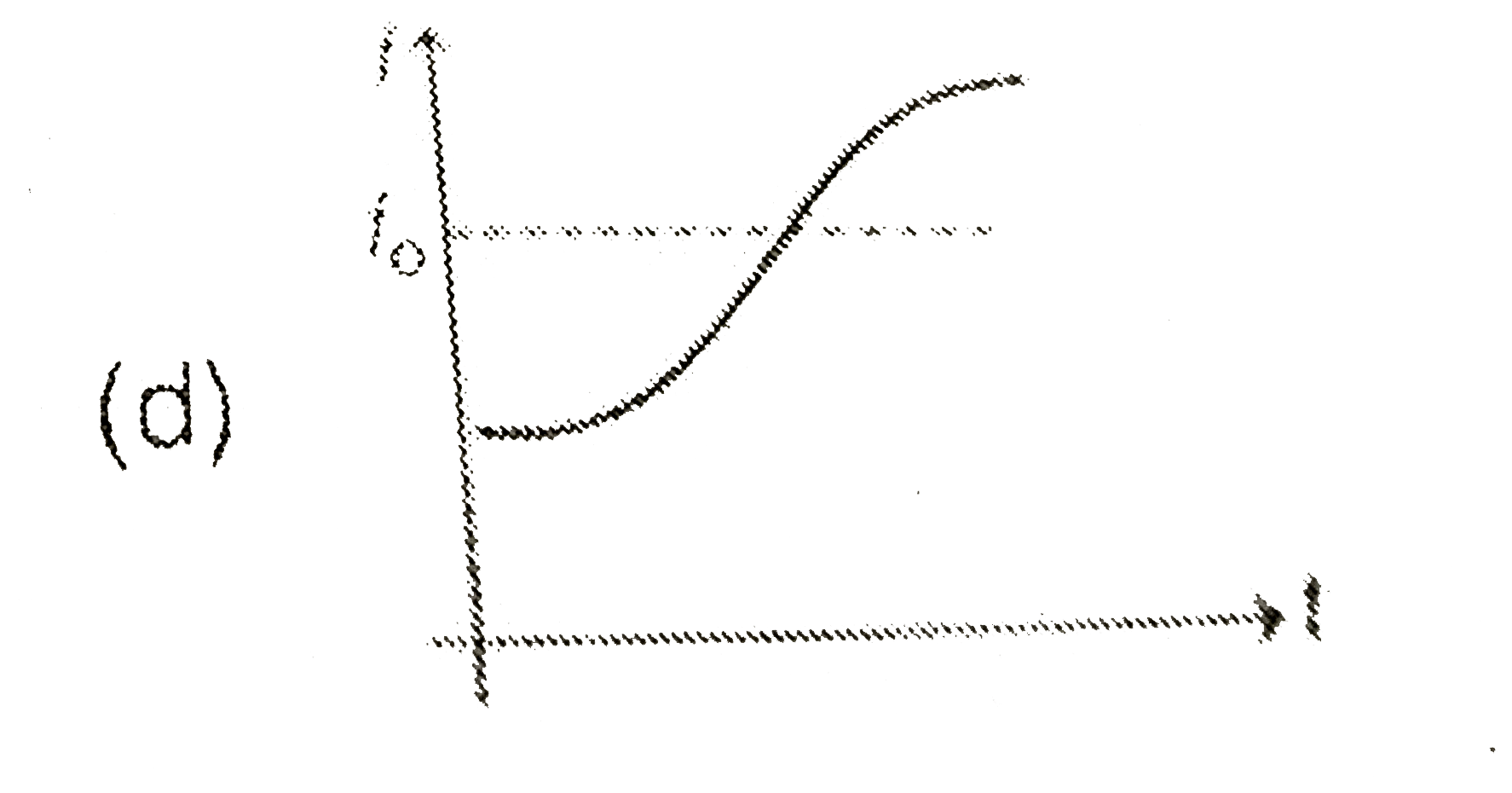A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVE MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise More Than One Option is Correct|23 VideosWAVE MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehion Type Questions|20 VideosWAVE MOTION
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAINS|50 VideosVECTORS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical enrances gallery|9 VideosWORK, ENERGY & POWER
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Comprehension Based|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-WAVE MOTION-ONLY ONE OPTION IS CORRECT
- A string is under tension sot that its length uncreased by 1/n times ...
Text Solution
|
- the frequency of a sonometer wire is 100 Hz. When the weight producing...
Text Solution
|
- source and observer both start moving simultaneously from origion one ...
Text Solution
|
- An observer starts moving with unifrom acceleration a towards a statio...
Text Solution
|
- Speed of sound wave is v. If a reflector moves towards a stationary so...
Text Solution
|
- A train is moving with a constant speed along a circular track. The en...
Text Solution
|
- A conveyor belt moves to the right with speed v=300 m/min. A pieman pu...
Text Solution
|
- Equations of two progressive waves are given by y(1) = asin (omegat +p...
Text Solution
|
- A transverse sine wave of amplitude 10 cm and wavelength 200 cm travel...
Text Solution
|
- A string of mass 0.2 kg/m and length l= 0.6 m is fixed at both ends a...
Text Solution
|
- A string fixed at both is vibrating in the lowest mode of vibration fo...
Text Solution
|
- two sound waves moves in the same direction .if the average power tran...
Text Solution
|
- the fundamental frequency of a sonometer wire of length is f(0).A brid...
Text Solution
|
- in a sine wave ,postive of different particles at time t=0 is shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A detector is released from rest over a source of sound of frequency f...
Text Solution
|
- A standing wave is maintained in a homogeneous string of cross - secti...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 Hz sinusoidal wave is travelling in the positve x - direaction a...
Text Solution
|
- At t=0 , observer and source are at same place. Now the source is proj...
Text Solution
|
- there are three strings RP, Pqand QS as shown. Their mass and length a...
Text Solution
|
- minimum frequency of audible sound is 20 Hz and maximum frequency is 2...
Text Solution
|