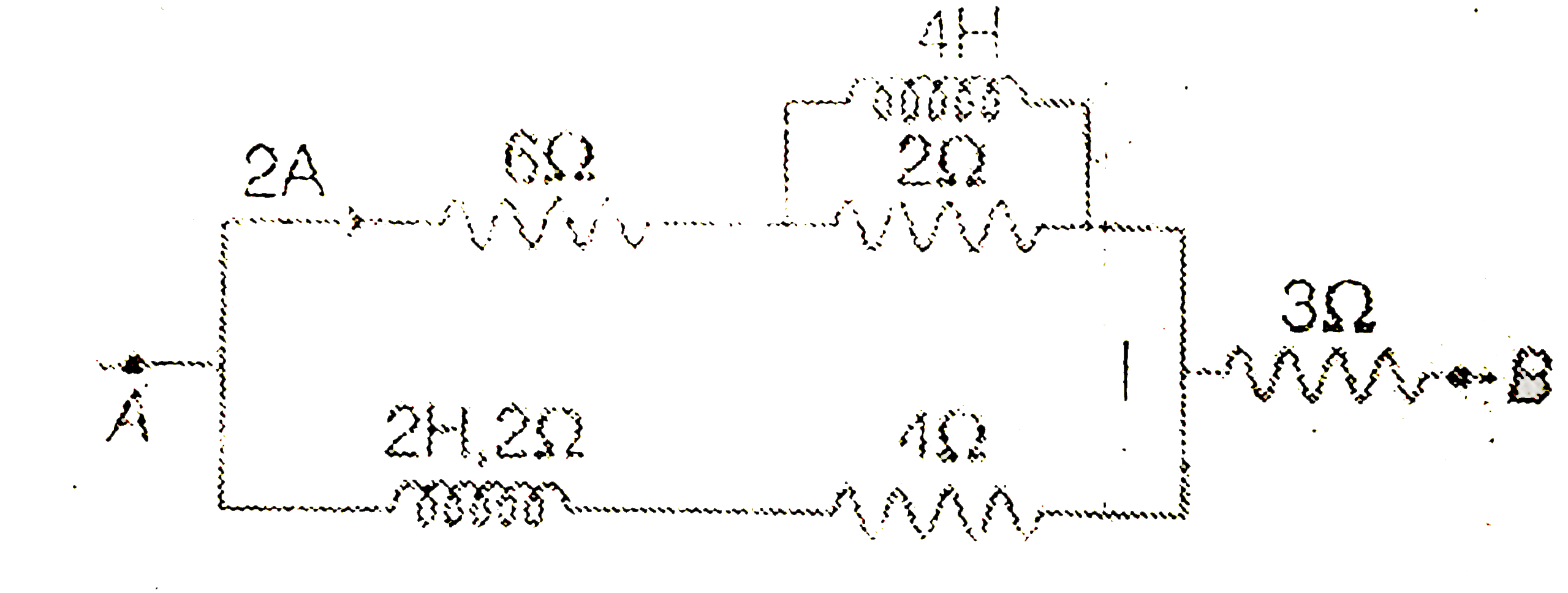A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-All Questions
- An ideal gas mixture filled inside a balloon expands according to the ...
Text Solution
|
- Ideal gas is taken through the process shown in the figure :
Text Solution
|
- Find V(A)-V(B) in steady state
Text Solution
|
- The specific heat of many solids at low temperatures varies with absol...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the volume thermal expansion coefficient for an ideal gas at...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform solid brass sphere is rotating with angular speed omega0 abo...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process p=(p(0))/(1+((V(0))/(V))...
Text Solution
|
- P-V diagram of a diatomic gas is a straight line passing through origi...
Text Solution
|
- The root mean spuare (rms) speed of hydrogen molecules at a certain te...
Text Solution
|
- Volume versus temperature graph of two moles of helium gas is as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas is shown in figure. ...
Text Solution
|
- Two moles of helium are mixed with n moles of hydrogen. The root mean ...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure P, Volume V and temperature T of a certain material are relat...
Text Solution
|
- Pressure versus density graph of an ideal gas is shown in figure
Text Solution
|
- One end of conducting rod is maintained at temperature 50^(@)C and at ...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between U, P and V for an iodeal gas is U=2+3PV. What is ...
Text Solution
|
- The specific heats of argon at constant pressure and constant volume a...
Text Solution
|
- Temperature of 1 mole of an ideal gas is increased from 300K to 310K u...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal monatomic gas at temperature T0 expands slowly ...
Text Solution
|
- If the ratio of specific heat of a gas at constant pressure to that at...
Text Solution
|