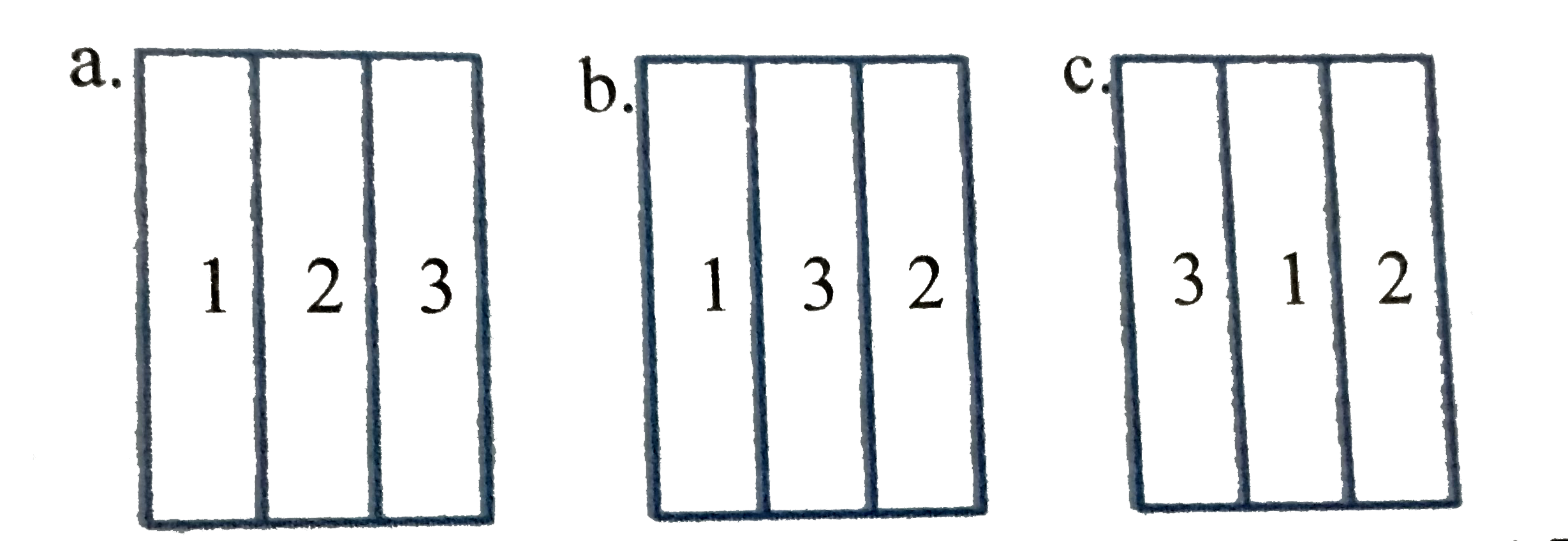
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-All Questions
- A thermal insulated vessel contains some water at 0^(@)C. The vessel i...
Text Solution
|
- The temperature drop through each layer of a two layer furnace wall is...
Text Solution
|
- Three different arrangemnets of matrials 1 and 2,3 to from a wall Thre...
Text Solution
|
- On a pT diagram, a cyclic process is performed as shown. Where is the ...
Text Solution
|
- A monoatomic ideal is used as the working substance for the carnot cyc...
Text Solution
|
- Figure illustrates a cycle conducted with n moles of an ideal gas. In ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a diatomic gas undergoes a process P = P(0)//[1 + (V//V(0)...
Text Solution
|
- 3 moles of an ideal mono atomic gas performs a cycle as shown in fig. ...
Text Solution
|
- Given T-p curve for three processes. Work done in process 1, 2 and 3 (...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two flasks connected to each other. The volume of the fla...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder piston of mass M sides smoothlly inside a long cylinder clo...
Text Solution
|
- A 1-L flask contains some mercury. It is found that at different tempe...
Text Solution
|
- A point source of heat of power P is placed at the centre of a spheric...
Text Solution
|
- A fixed chamber isolated from surrounding is divided into equal halves...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the VT diagram for helium gas in a cyclic process. Find t...
Text Solution
|
- The state of an ideal gas is changed through an isothermal process at ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas undergoes a process in which co-efficient of volume expan...
Text Solution
|
- A solid body X of very large heat capacity is kept in an atmosphere wh...
Text Solution
|
- A black body emits radiation at the rate P when its temperature is T. ...
Text Solution
|
- Where does a body weigh more – at the surface of the earth or in a min...
Text Solution
|