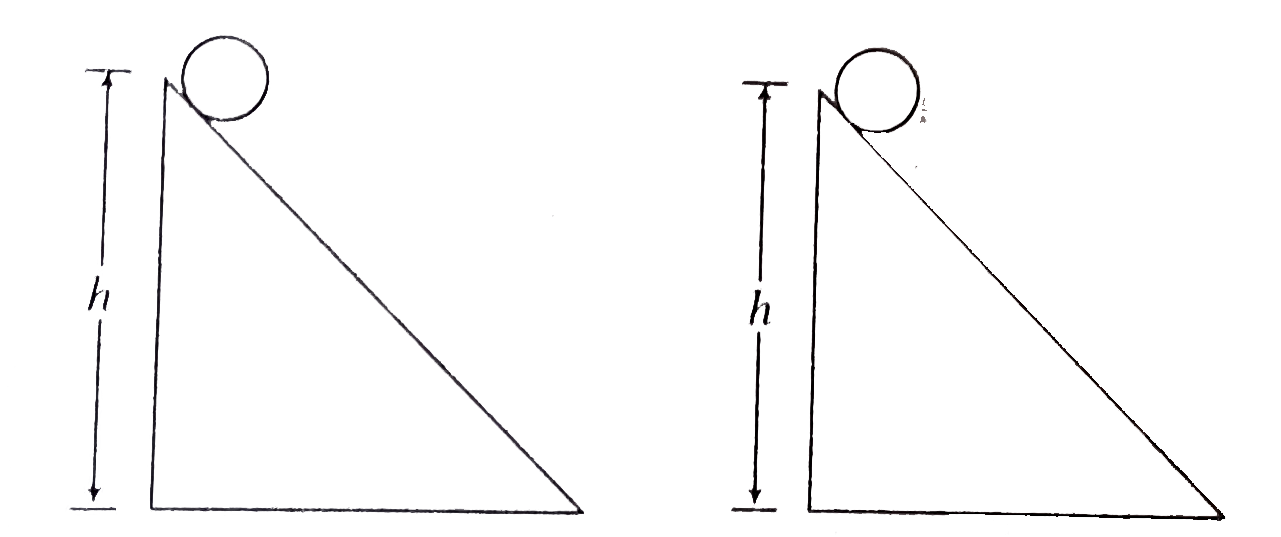A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ROTATION-(B) Chapter Exercises
- Assertion : The condition of equilibrium for a rigid body is Transla...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two axes AB and CD are as shown in figure. Given figure is...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If a particle moves with a constant velocity, then angular...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two identical solid spheres are rotated frm rest to same a...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A ring and a disc of same mass and radius begin to roll wi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A sphere is placed in pure rolling condition over a rough ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In rotational plus translational motion of a rigid body, d...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Angular momentum of sun and planet system about any point ...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Moment of inertia about an axis passing throught centre of...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A solid sphere cannot roll without slipping on smooth hori...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Speed of any point on rigid body executing rolling motion...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A solid sphere and a ring of same mass and radius are rele...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A uniform disc of radius R is performing impure rolling mo...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Two identical spherical balls are released from two inclin...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : A solid and a hollow sphere both of equal masses and radii...
Text Solution
|
- If radius if earth is reduced to half without changing its mass, then ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rolls on ground without slipping. Velocity of centre of mass is...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere is rotating about an axis shown in figure. An insect fo...
Text Solution
|
- Four rods of equal length l and mass m each forms a square as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- A semi-circular ring has mass m and radius R as shown in figure. Let I...
Text Solution
|