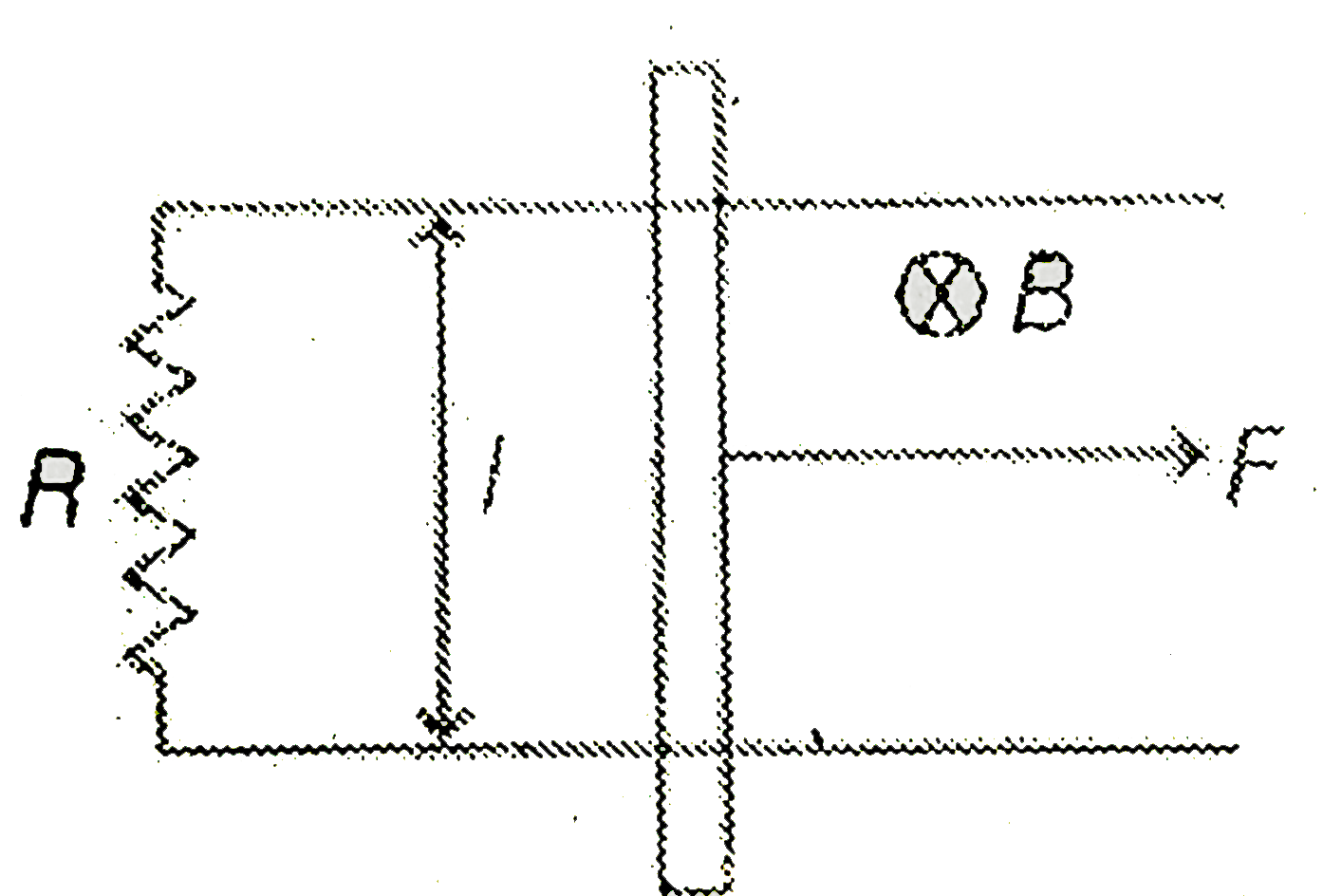
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-ALTERNATING CURRENT-JEE MAIN
- In the given arrangement, the loop is moved with consisant velocity in...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field existsin region given by vec(B) = 3 hat(i) + ...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force is being applied on a road of length 'l' kept at rest...
Text Solution
|
- Figures shows a square loop of side 1m and resistance 1Omega. The magn...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of fixed length is wound on a solenoid of length l and radius r...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, let i(1) be the current drawn battery at time t=...
Text Solution
|
- In a series L-R growth circuit, if maximum current and maximum voltage...
Text Solution
|
- A resistance is connected to a capacitor in AC are the phase differece...
Text Solution
|
- A reacangular loop if size (2m xx 1m) is placed in x-y plane. A unifor...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of a circular ring is changing with time and the coil is placed...
Text Solution
|
- r.m.s. value of current i=3+4sin (omegat+pi//3) is
Text Solution
|
- An AC voltage of V=220sqrt2 sin (100pit+(pi)/(2))V is applied across a...
Text Solution
|
- A direct current of 2 A and an alternating current having a maximum va...
Text Solution
|
- By what percentage the impedance in an AC series circuit should be inc...
Text Solution
|
- A power transformer (step up) with an 1:8 turns ratio has 60 Hz,120 V ...
Text Solution
|
- A choke coil has
Text Solution
|
- Comparing the L-C oscillations with the oscillations of a spring-block...
Text Solution
|
- A capacitor of capacity 2muF is changed to a potential different of 12...
Text Solution
|
- The power factor of the circuit in fig. is 1//sqrt(2). The capacitance...
Text Solution
|
- An ac-circuit having supply voltage E consists of a resistor of resis...
Text Solution
|