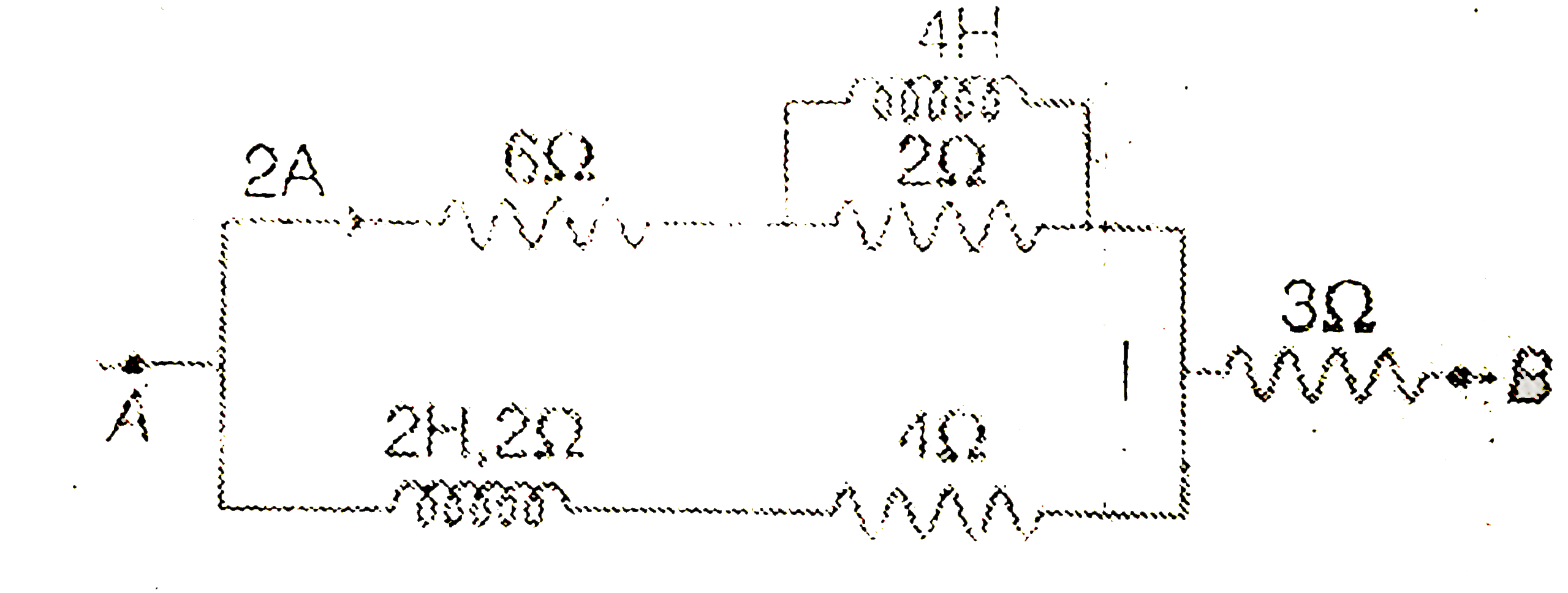A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Find V(A)-V(B) in steady state
Text Solution
|
- In the system is in steady state. Then a. V(A)-V(B)="" b. V(B)-V(C...
Text Solution
|
- V(A)*V(B) for given figure in steady state is
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential difference between points A and B (V(B)-V(A)) in th...
Text Solution
|
- Find V(A)-V(B) in steady state
Text Solution
|
- Find out following (i) V(A)-V(B) (ii) V(B)-V(C) (iii) V(C)-V(A) (iv) V...
Text Solution
|
- Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in the figure betw...
Text Solution
|
- संलग्न चित्र में एकसमान वैघुत क्षेत्र E=10 वोल्ट/मीटर दर्शाया गया है। ...
Text Solution
|
- प्रदर्शित परिपथ में A व B के bich तुल्ये प्रतिरोध ज्ञात कीजिएः यदि V(A...
Text Solution
|