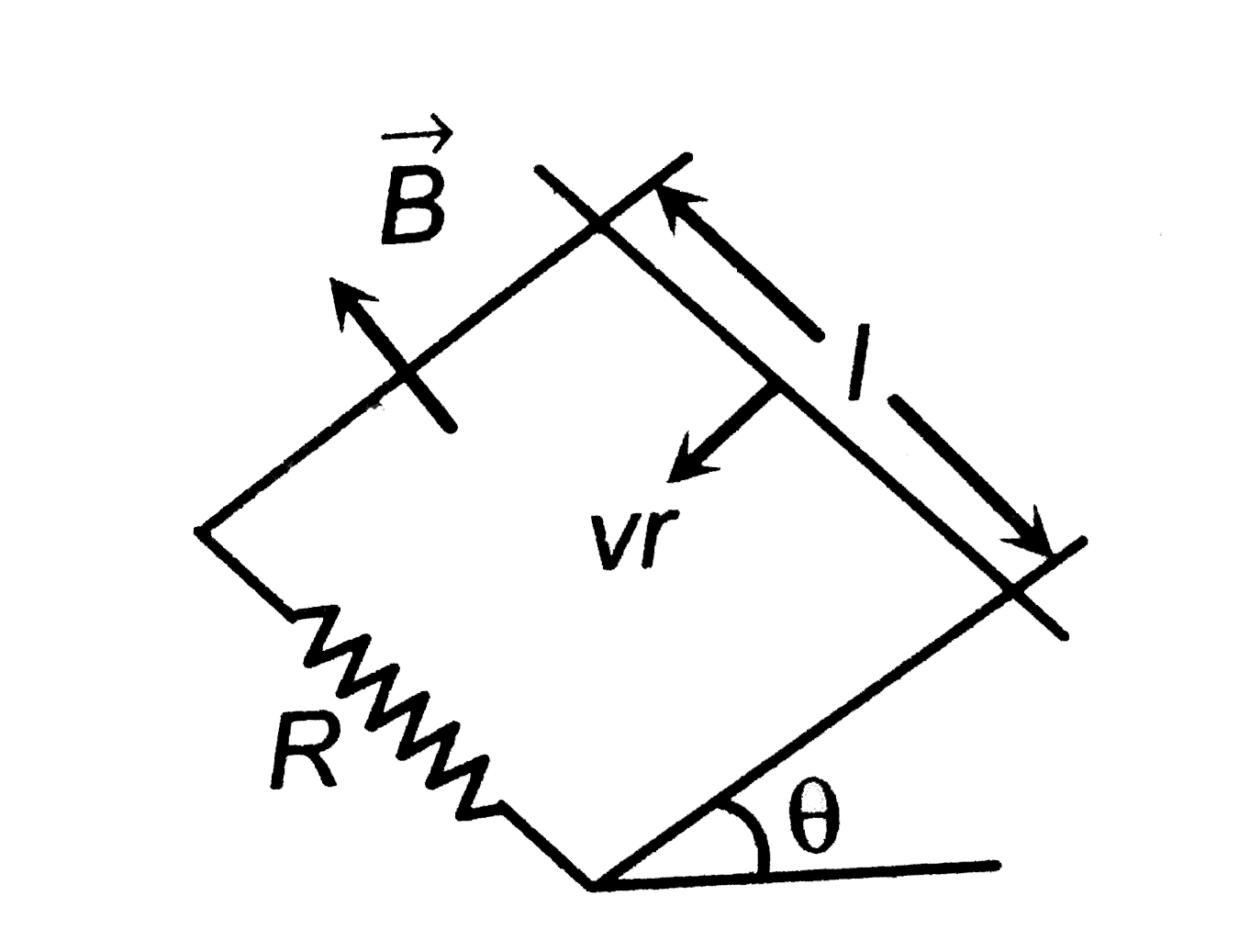
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rai...
Text Solution
|
- Shows a rod of length l and resistance r moving on two rails shorted b...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of mass m , length l and resistance R is sliding down on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- A copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rai...
Text Solution
|
- A copper rod of mass m rests on two horizontal rails distance L apart ...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of long, smooth, parallel, horizontal, conducting rails are joi...
Text Solution
|
- A copper bar of mass m sides under gravity on two smooth parallel ra...
Text Solution
|
- a copper rod of mass m slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rai...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a s...
Text Solution
|