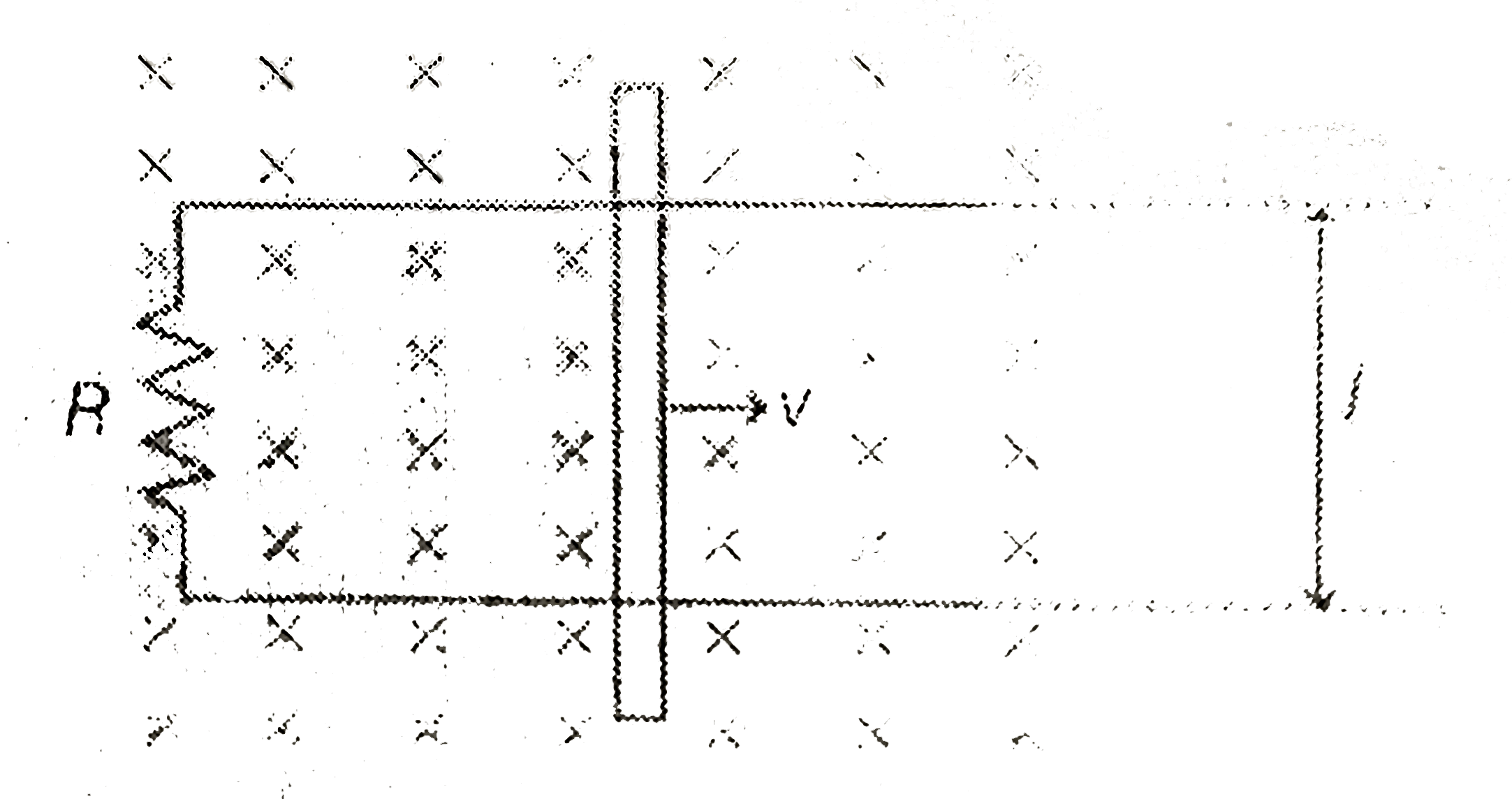A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conducting bar is slid at a constant velocity v along two conducting...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic fie...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length l slides at constant velocity v on two para...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar is slid at a constant velocity v along two conducting...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar is slid at a constant velocity v along two conducting...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar is slid at a constant velocity v along two conducting...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length l is moving in a transverse magnetic field ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length I and velocity v moves in a magnetic field ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic fi...
Text Solution
|