Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
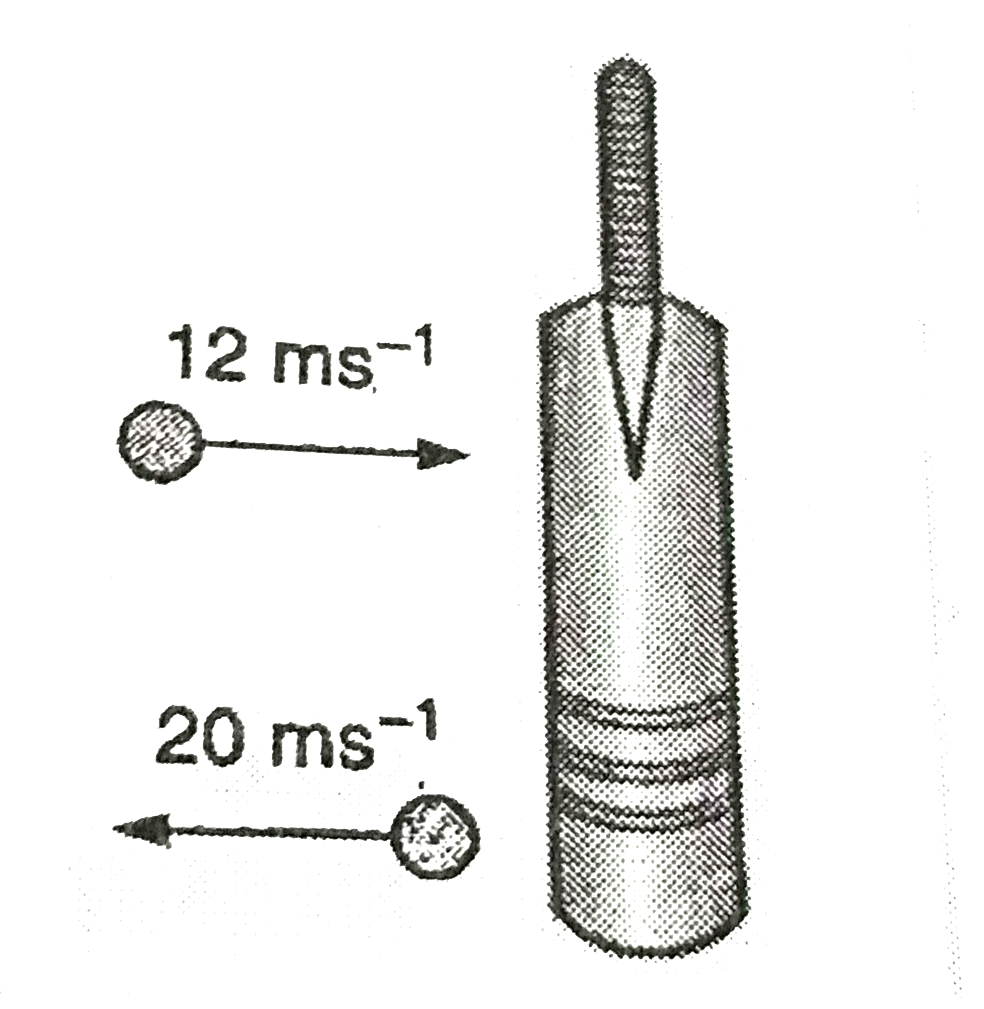
- A cricket ball of mass 150 g is moving with a speed of 12ms^(-1) and i...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150 kg is moving with a velocity of 12 m//s and...
Text Solution
|
- cricket ball of mass 150 g is moving with a velocity of 12m//sec and i...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150 g is moving with a speed of 12ms^(-1) and i...
Text Solution
|
- A 150 g ball, moving horizontally at 20m/s was hit straight back to bo...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150g is moving with a velocity of 12 m/s and is...
Text Solution
|
- A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a speed of 12 ms^(-1) is hit ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 100 g is moving with a velocity of 10 ms^(-1) . On bein...
Text Solution
|
- একজন ক্রিকেটার দক্ষিনদিকে 30m/s বেগে গতিশীল একটি বলকে ব্যাটের আঘাতে উত...
Text Solution
|