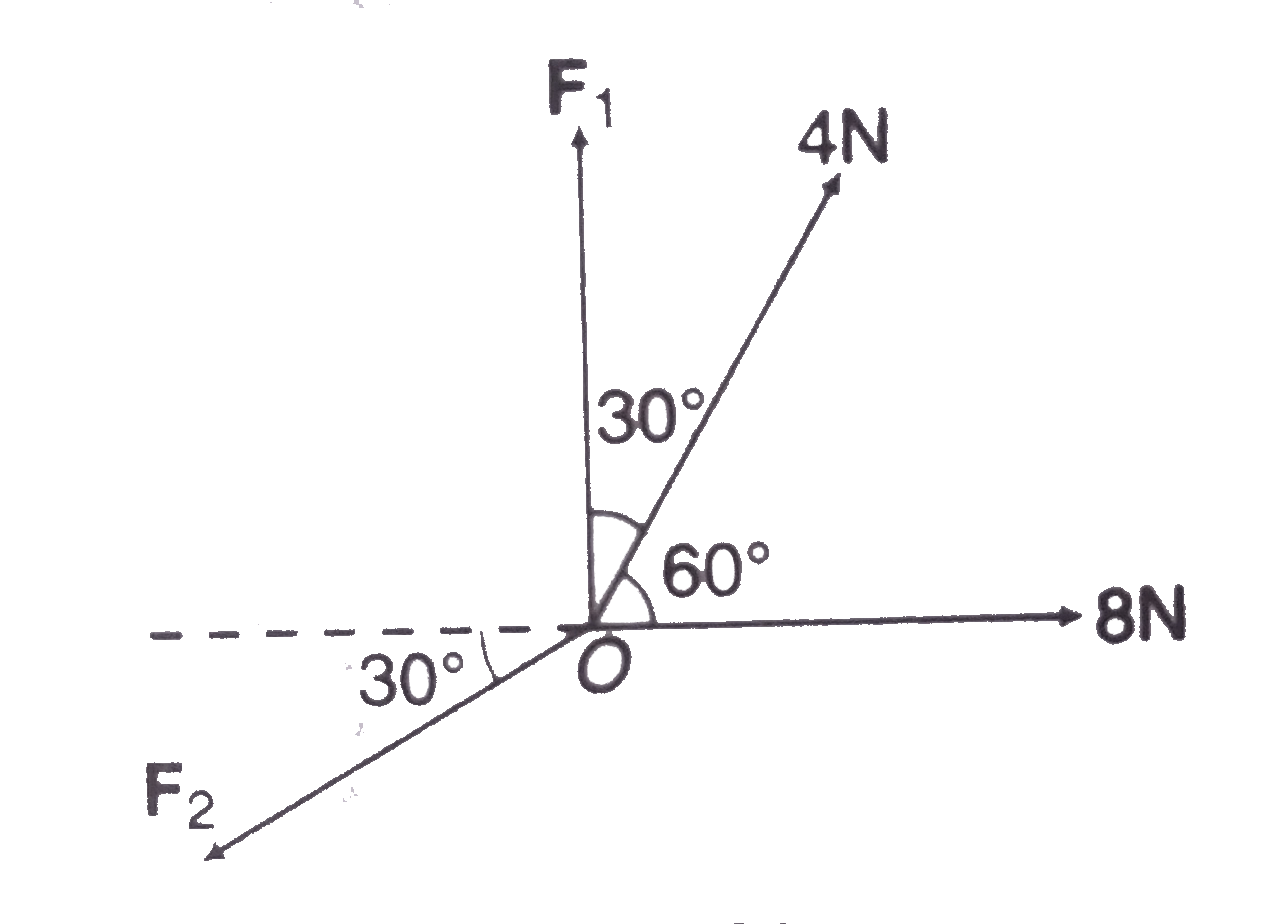
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An object is in equilibrium under four concurrent forces in the direct...
Text Solution
|
- An object is in equilibrium under four concurrent forces in the direct...
Text Solution
|
- Three concurrent force are F(1),F(2) and F(3) . Angle between F(1) and...
Text Solution
|
- There are four force acting at a point p produced by strings as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- There are four forces acting at a point O produced by strings as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Four forces act on a particle as shown in the figure such that net for...
Text Solution
|
- Three forces F(1), F(2) and F(3) act on an object simultaneously. Thes...
Text Solution
|
- Two forces of mangitude F(1) and F(2) are acting on an object.The magn...
Text Solution
|
- When three forces F(1), F(2) And F(3) Is acting on an object of mass m...
Text Solution
|