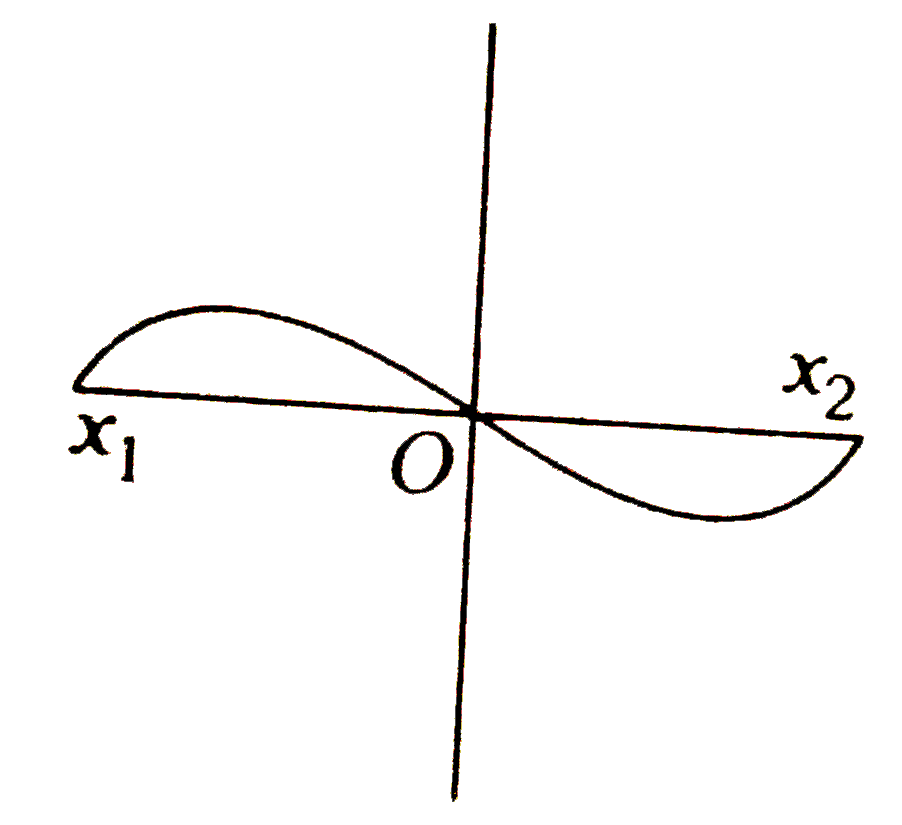
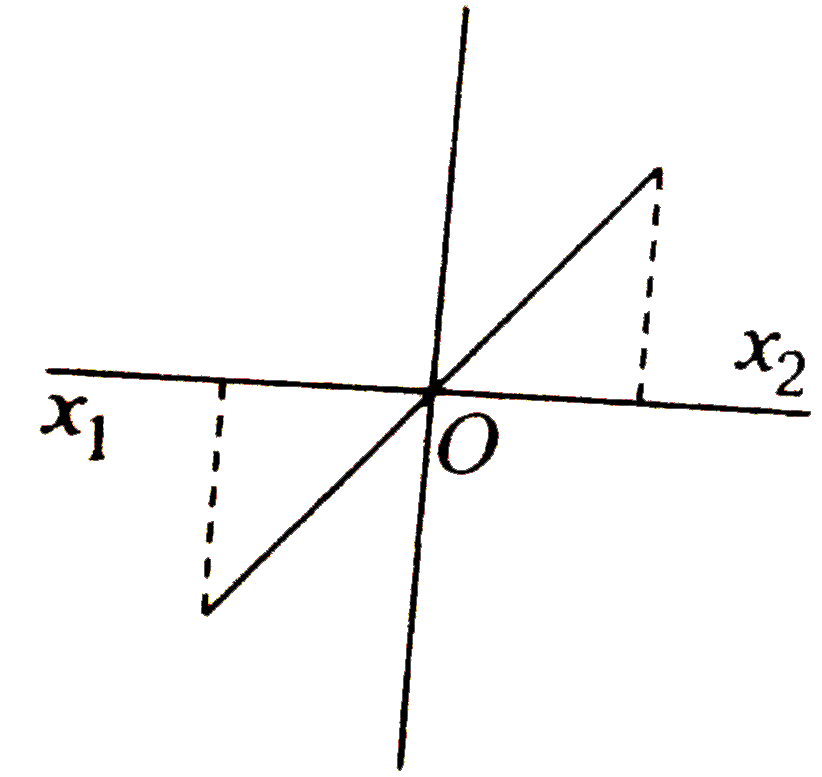
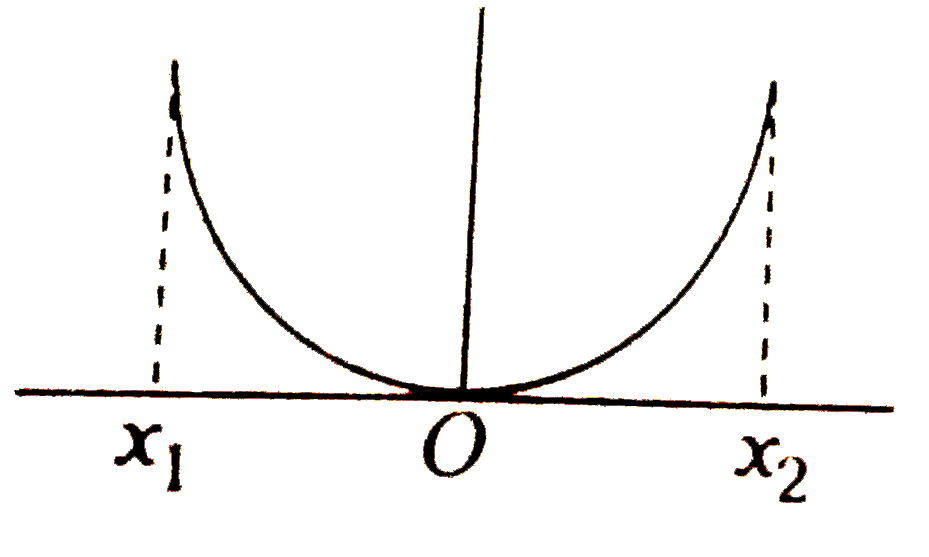
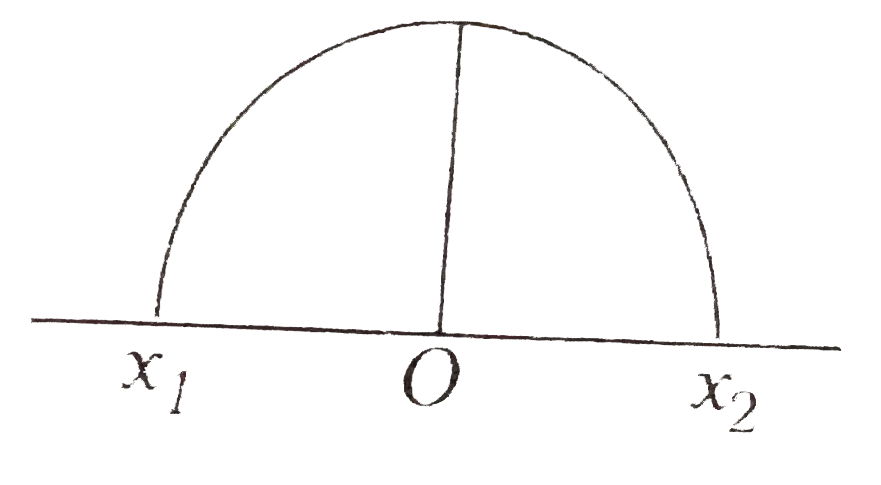
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A particle of mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion between po...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 2 kg moves in simple harmonic motion and its potent...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion between po...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion between po...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves with simple harmonic motion in a straight line. When ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m executes simple harmonic motion with amplitude a ...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान m का एक कण दो बिंदुओं x(1) और x(2) के बीच सरल आवर्त गति में...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान m का एक कण, साम्य स्थिति O बिन्दुओं x(1) व x(2) के मध्य सरल ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' executes simple harmonic motion with amplitude ...
Text Solution
|