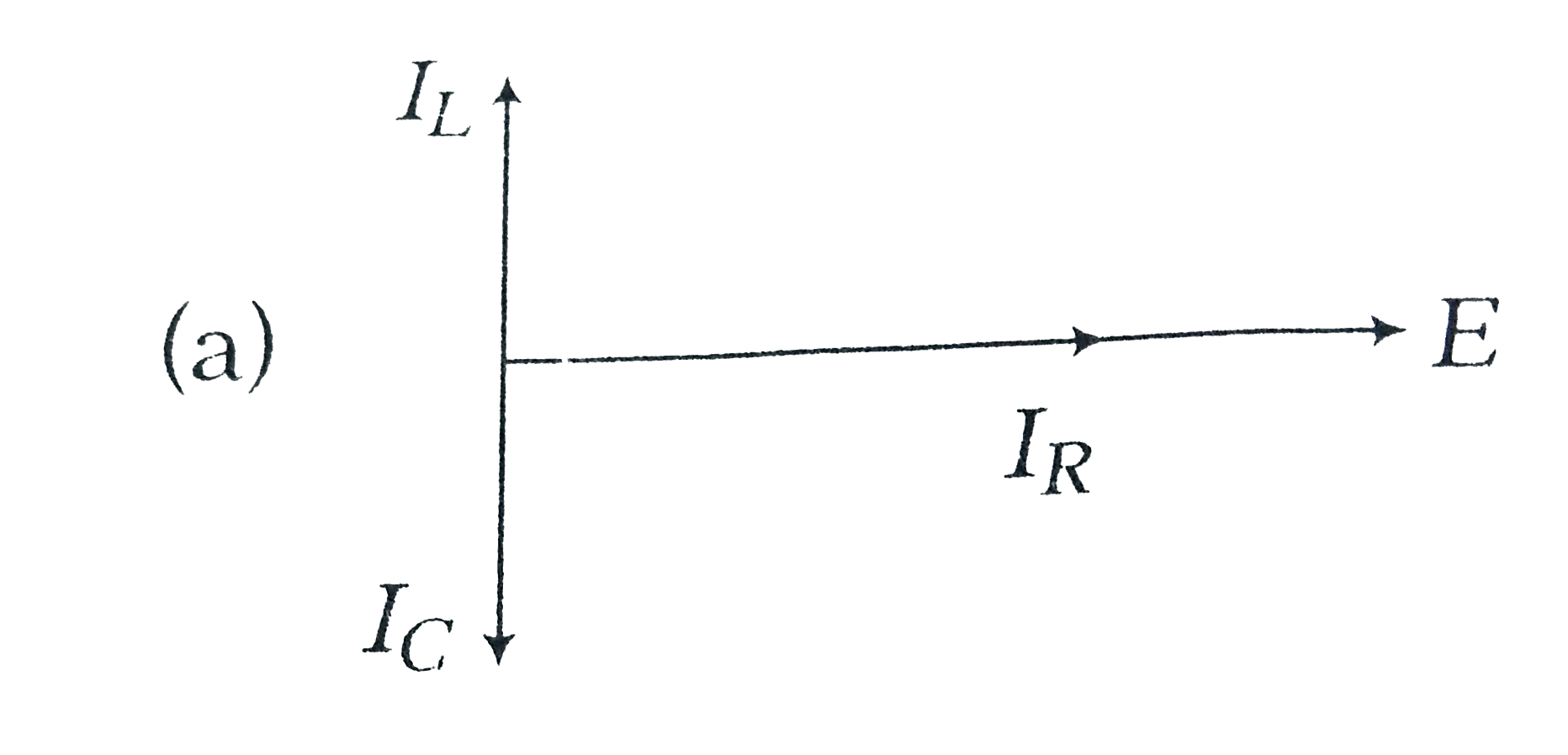
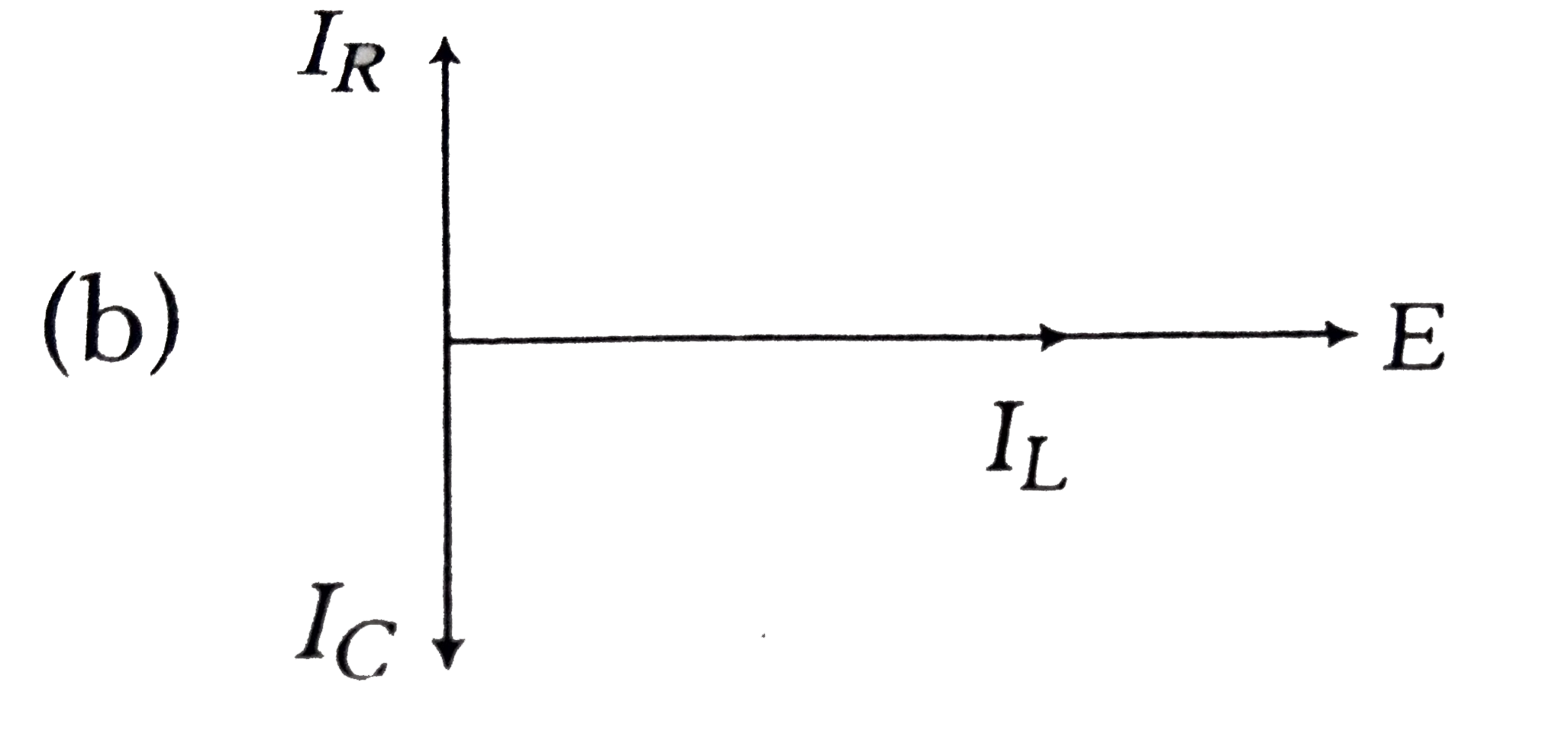
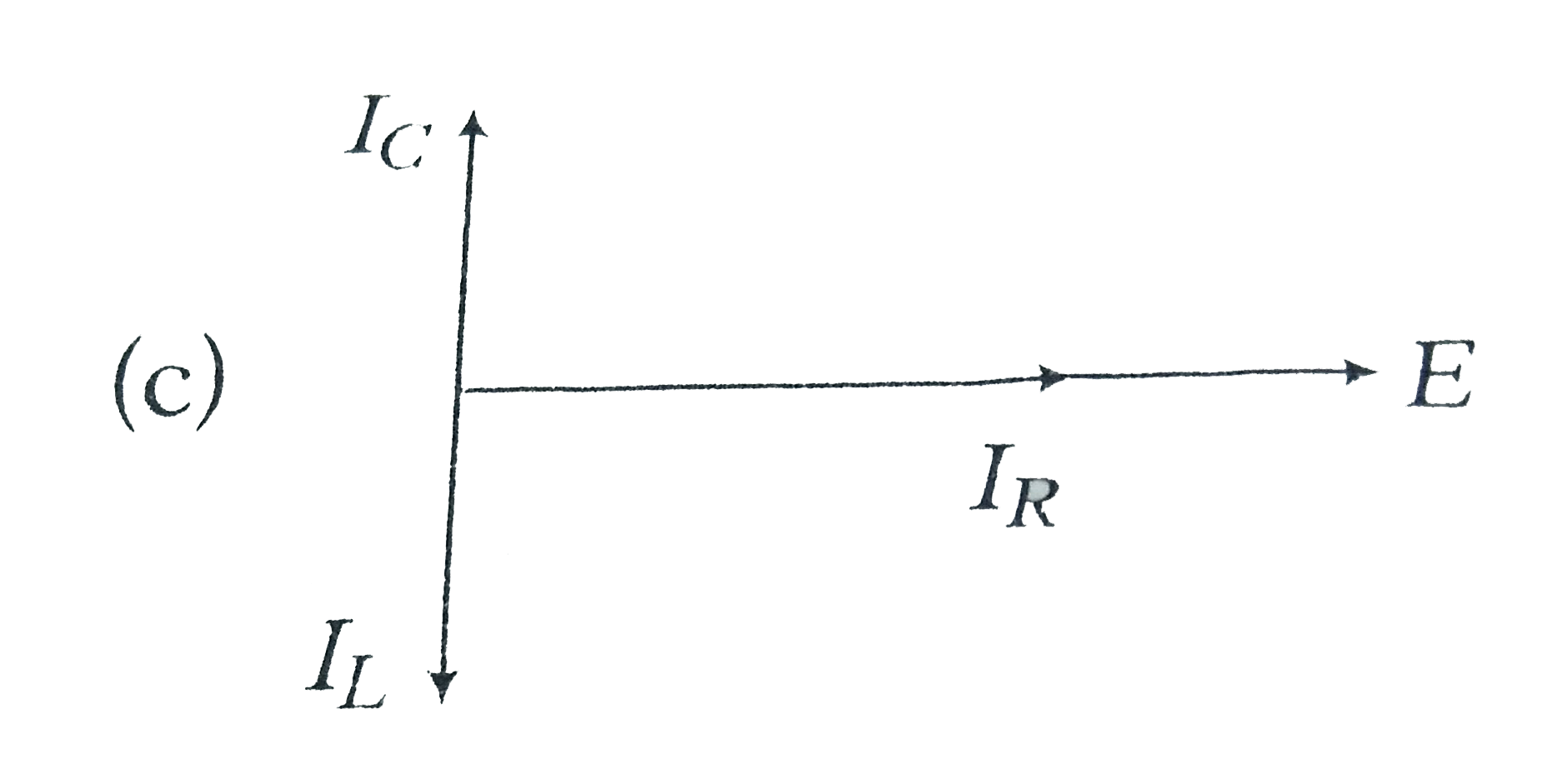
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An alternating emf is applied across a parallel combination of a resis...
Text Solution
|
- An alternating emf is applied across a parallel combination of a resis...
Text Solution
|
- The correct IUPAC name of the given compound is I-underset(F)underset(...
Text Solution
|
- Acylium cation has two resonating sturctures (I) and (II), R-underset(...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal resistance R, ideal inductance L , ideal capacitance C and AC...
Text Solution
|
- (i). R-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH(2)COOHunderset(Delta)overset(NaH...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will be oxidised by HIO(4)? (A) R-underset(O)...
Text Solution
|
- Identify B, C, D and E in the following reactions CH3-underset(CH3)und...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the correct configuration of following structures : unde...
Text Solution
|