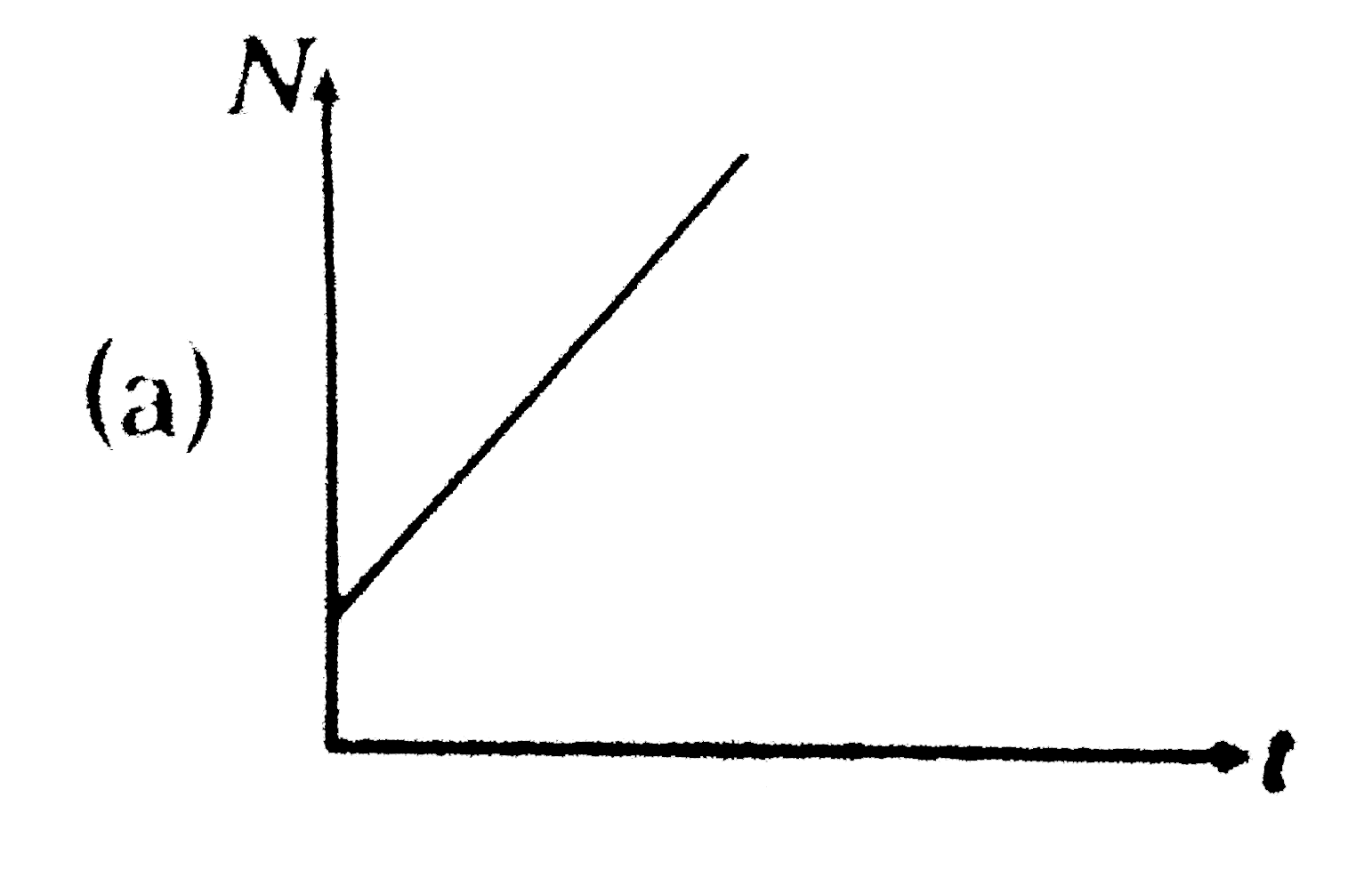
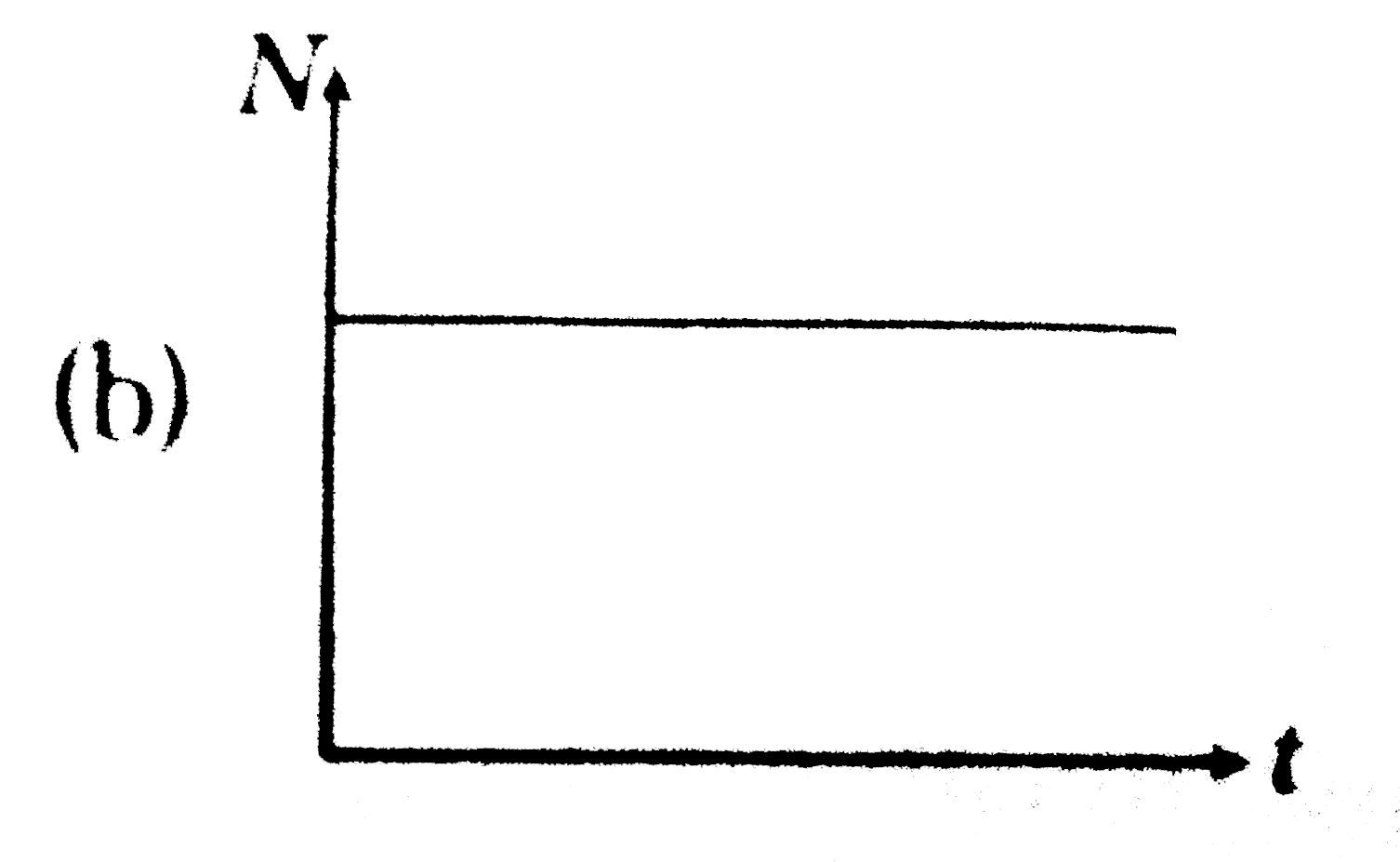
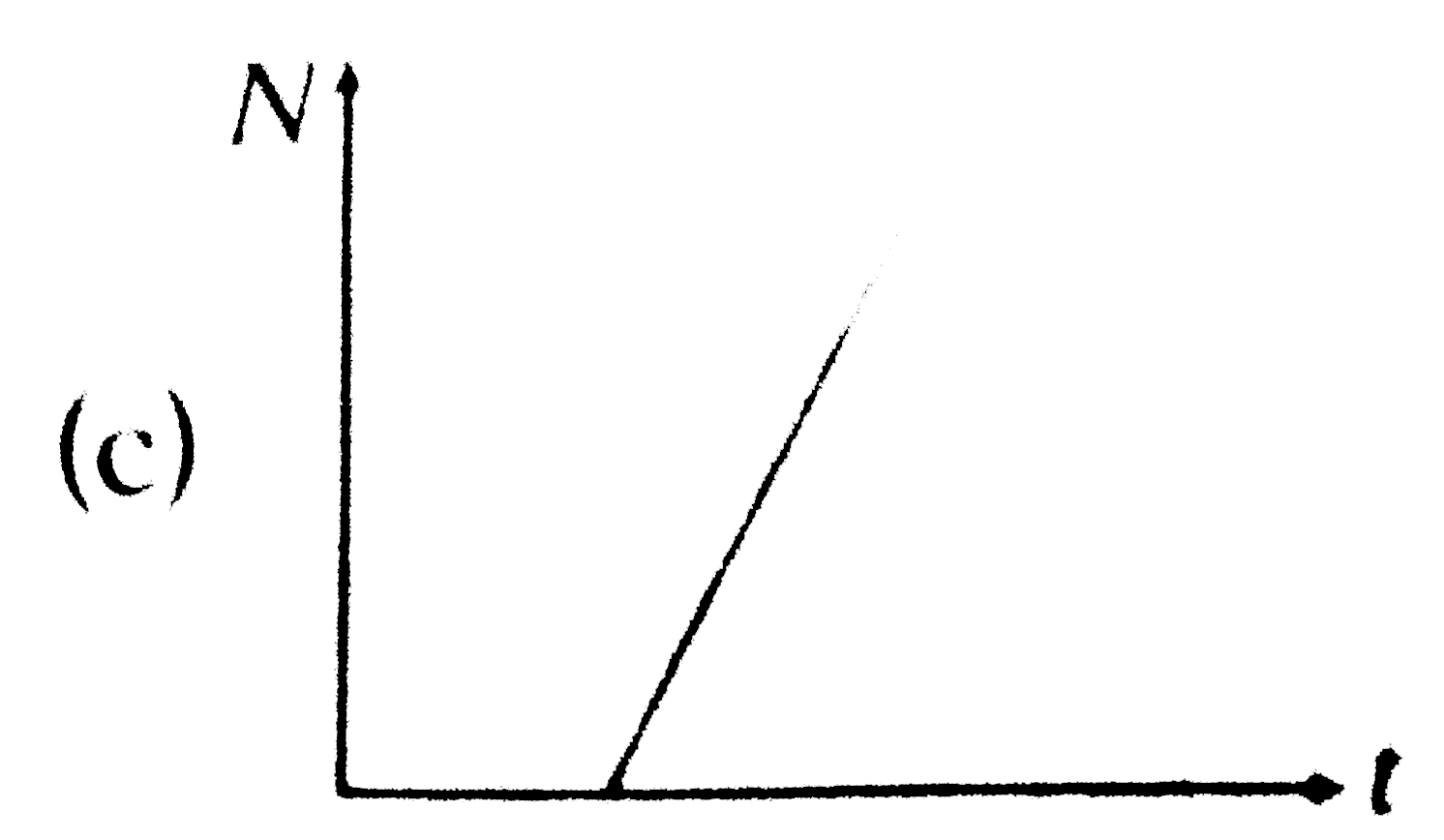
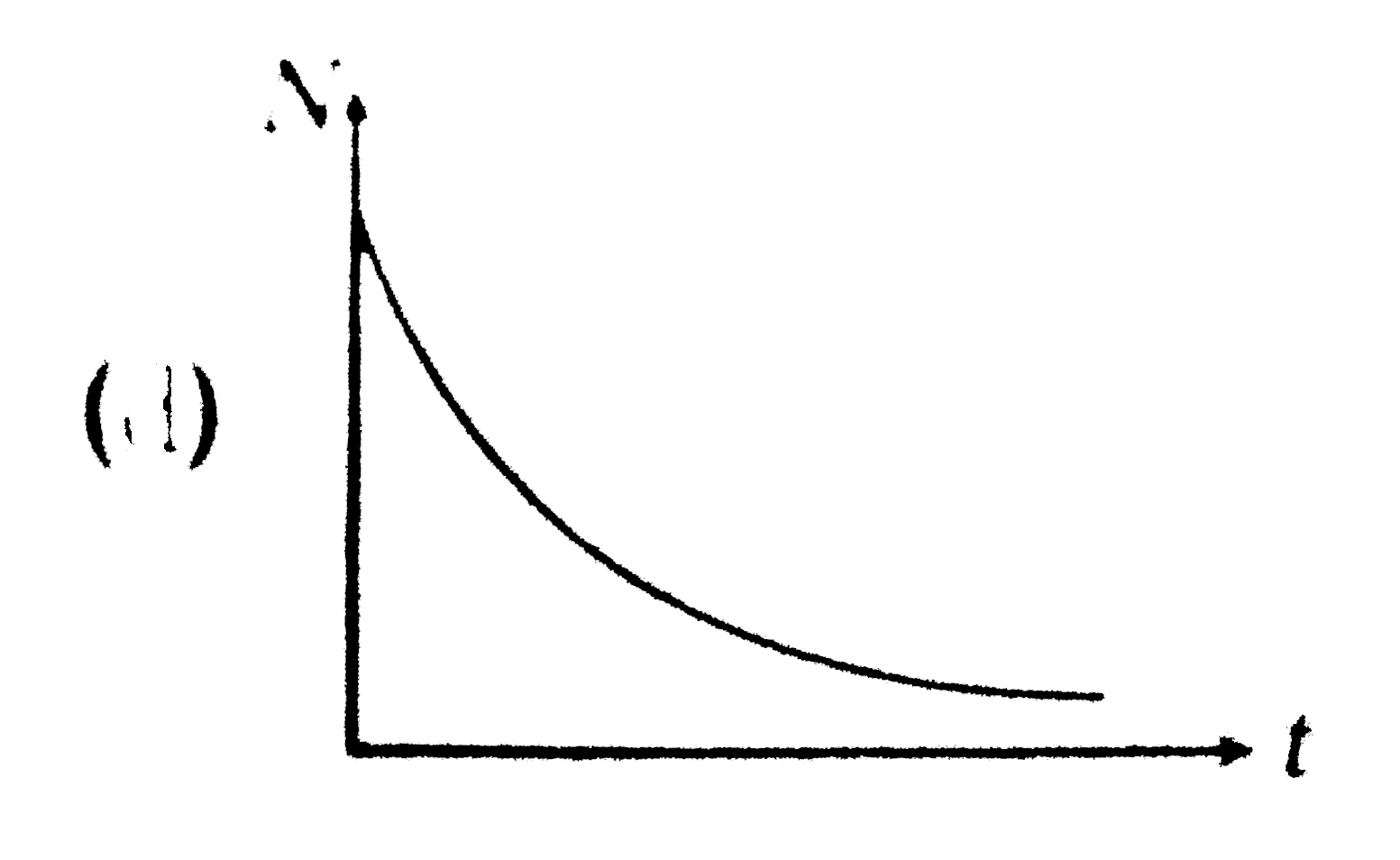
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
NUCLEI
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise B Medical entrance special format questions|9 VideosNUCLEI
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise MATCH THE COLUMNS|4 VideosNUCLEI
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise CHECK POINT 13.3|15 VideosMODERN PHYSICS - 2
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|10 VideosRAY OPTICS
DC PANDEY ENGLISH|Exercise Medical entrance gallary|76 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-NUCLEI-CHAPTER EXERCISES
- A radioactive sample has N0 active at t = 0 . If the rate of disintegr...
Text Solution
|
- The plot of the number (N) of decayed atoms versus activity (R) of a r...
Text Solution
|
- The graph between the instantaneous concentration (N) of a radioactive...
Text Solution
|
- Two redioactive materials X(1)andX(2) have decay constants 10lamdaandl...
Text Solution
|
- Two radioactive nuclei A and B are taken with their disintegration con...
Text Solution
|
- What is the binding energy per nucleon in ""2He^4 ? Given , Mass of ...
Text Solution
|
- A radio istoper X with a half-life 1.4xx10^(8) yr decays of Y which is...
Text Solution
|
- The energy released by the fission of a single uranium nucleus is 200 ...
Text Solution
|
- A common example of beta-"decay" is ""(15)P^(32)to""(16)P^(32)+x+y ...
Text Solution
|
- A nucleus with Z =92 emits the following in a sequence: alpha,beta^(...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B of equal masses are placed on rough incli...
Text Solution
|
- Tritium is an isotope of hydrogen whose nucleus triton contains 2 neut...
Text Solution
|
- The gravitational force between a H-atom and another particle of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- In a sample of radioactive material, what fraction of initial number o...
Text Solution
|
- In a radioactive sample, the fraction of initial number of redioactive...
Text Solution
|
- At any instant, the ratio of the amounts of two radioactive substance ...
Text Solution
|
- A radioactive isotope X with half-life 1.5xx10^(9) yr decays into a st...
Text Solution
|
- Find the decay rate of the substance having 4xx10^15 atoms. Half life ...
Text Solution
|
- The half life of radioactive element is 20 min. The time interval betw...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are two radioactive substance whose half - lives are 1 and 2 y...
Text Solution
|