Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OSWAAL PUBLICATION-SOLVED PAPER II PUC APRIL-2016 -PART-D
- Derive an integrated rate equation for the rate constant of a zero ord...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a graph of potential energy v/s reaction co-ordinate showing the ...
Text Solution
|
- Mention any three differences between lyophilic and lyophobic colloids...
Text Solution
|
- What is heterogeneous catalysis ? Give an example.
Text Solution
|
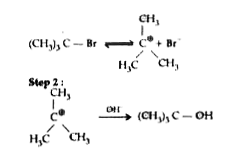
- Explain the mechanism of SN1 reaction taking 2-bromo-2-methyl propane ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain wurtz-Fitting's reaction
Text Solution
|
- Write the general formula of Grignard reagent
Text Solution
|
- How is phenol manufactured by Cumene process?
Text Solution
|
- Among alcohols and phenols which one is more acidic?
Text Solution
|
- Explain the mechanism of addition of HCN to a carbonyl group in presen...
Text Solution
|
- How is bezamide obtained from benzoic acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain Carbyl amine reaction
Text Solution
|
- What is the action of bromine water on Benzenamine (Aniline) at room t...
Text Solution
|
- The pkb values of Ammonia, methanamine and Benzenamic (aniline) are 4....
Text Solution
|
- How do you show that glucose contains a linear chain of six carbon ato...
Text Solution
|
- What are essential amino acids?Is glycine an essential amino acid ?
Text Solution
|
- Write the general formula of Zwitter ionic form of an amino acid
Text Solution
|
- Explain addition polymerisation with an example.
Text Solution
|
- Name the monomers usedl in the manufacture of Nylon-6, 6.
Text Solution
|
- Write the partial structure of Neoprene
Text Solution
|